Insulators turn up the heat on quantum bits
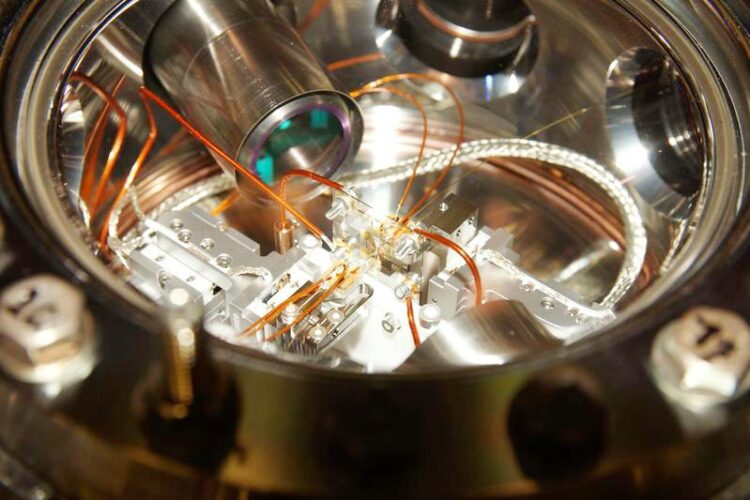
In the ion trap, the distance between the ions and optics can be precisely adjusted.
Uni Innsbruck
Physicists have long suspected that dielectric materials may significantly disrupt ion-trap quantum computers. Now, researchers led by Tracy Northup have developed a new method to quantify this source of error for the first time. For the future operation of quantum computers with very many quantum bits, such noise sources need to be eliminated already during the design process if possible.
Quantum technologies are based on quantum properties of light, electrons, and atoms. In recent decades, scientists have learned to master these phenomena and exploit them in applications. Thus, the construction of a quantum computer for commercial applications is also coming within reach. One of the emerging technologies that is currently being advanced very successfully is ion trap quantum computers. Here, charged particles are trapped with electromagnetic fields in a vacuum chamber and prepared in such a way that they can serve as carriers for information and be used for computing, which includes cooling them to the lowest temperatures permitted by quantum mechanics.

View into the vacuum chamber where the ion trap is isolated from external noise.
Uni Innsbruck
However, the quantum mechanical properties exploited in this process are highly error prone. Even the smallest deficiencies can heat up the strongly cooled particles and thereby lead to errors in the processing of quantum information. Possible sources of such faults are weakly conducting or non-conducting materials, which are used, for example, as insulators in a metallic ion trap, or optics, which are necessary for coupling ions with laser light. “Even for ion traps made exclusively of metal, oxide layers on the metals would cause such failures,” explains Tracy Northup at the Department of Experimental Physics of the University of Innsbruck in Austria. Northups team together with collaborators in Innsbruck and in the U.S. have found a way to determine the influence of dielectric materials on the charged particles in ion traps.
Experimentally confirmed
This was achieved because the Innsbruck quantum physicists have an ion trap in which they can precisely set the distance between the ions and dielectric optics. Based on an earlier proposal by Rainer Blatt’s group, the physicists computed the amount of noise caused by the dielectric material for this ion trap and compared it with data from experiment. “Theory and experiment agree very well, confirming that this method is well suited for determining the influence of dielectric materials on the ions,” explains Markus Teller from the Innsbruck team. To calculate the noise, the so-called fluctuation-dissipation theorem from statistical physics was used, which mathematically describes the response of a system in thermal equilibrium to a small external perturbation.
“In quantum computers, there are many possible sources of noise, and it is very difficult to sort out the exact sources,” says Tracy Northup. “Our method is the first to quantify the influence of dielectric materials in a given ion trap on the charged particles. In the future, designers of ion trap quantum computers will be able to assess this effect much more accurately and design their devices to minimize these perturbations.” After having successfully demonstrated the method on their own ion trap, the Innsbruck physicists now want to apply it to the ion traps of collaborators in the U.S. and Switzerland.
The research was financially supported by the Austrian Science Fund FWF and the European Union, among others. The results have been published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Markus Teller
Department of Experimental Physics
University of Innsbruck
phone: +43 512 507 52401
email: markus.teller@uibk.ac.at
web: https://www.uibk.ac.at/exphys/quantum-interfaces/
Originalpublikation:
Heating of a trapped ion induced by dielectric materials. Markus Teller, Dario A. Fioretto, Philip C. Holz, Philipp Schindler, Viktor Messerer, Klemens Schüppert, Yueyang Zou, Rainer Blatt, John Chiaverini, Jeremy Sage, and Tracy E. Northup. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 230505 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.230505 https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.230505
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


