Continental pirouettes
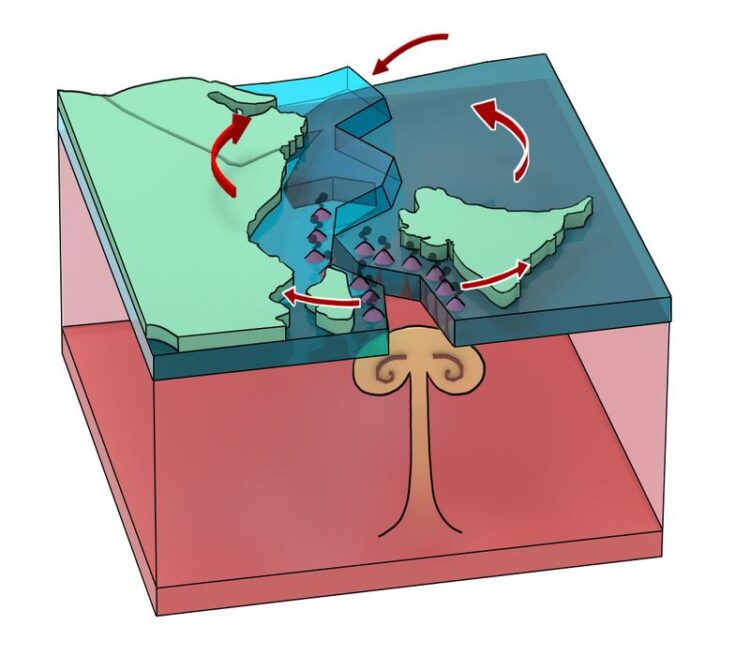
The 3-D illustration shows the so-called mantle plume feeding the super volcano which forced the plates apart. The arrows indicate the different movements.
(c) Alisha Steinberger / GFZ
Supervolcano fed from Earth’s mantle caused crustal plates to rotate.
The plates of the Earth’s crust perform complicated movements that can be attributed to quite simple mechanisms. That is the short version of the explanation of a rift that began to tear the world apart over a length of several thousand kilometers 105 million years ago. The scientific explanation appears today in the journal Nature Geoscience.
According to the paper, a super volcano split the Earth’s crust over a length of 7,500 kilometers, pushing the Indian Plate away from the African Plate. The cause was a “plume” in the Earth’s mantle, i.e. a surge of hot material that wells upwards like an atomic mushroom cloud in super slow motion. It has long been known that the Indian landmass thus made its way northward and bumped into Eurasia. But a seemingly counterintuitive east-west movement of the continental plates was also part of the process. This is supported by calculations by a team led by Dutch scientist Douwe van Hinsbergen (Utrecht University) and Bernhard Steinberger (GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences).
According to the findings, the Indian Plate did not simply move away from Africa, but rotated in the process. The reason for this is the subcontinent, whose land mass acts on the much larger continental plate like an axis around which the entire plate rotates. In the south, the scissors opened, in the north they closed – there, mountain-building processes and the subduction of crustal plates were induced.
This has dramatic effects up to the present time: The subduction processes continue and trigger earthquakes again and again in the Mediterranean region between Cyprus and Turkey. The traces of the plume and the supervolcano can still be identified today. They are flood basalts on Madagascar and in the southwest of India. They testify to immense volcanic activity fed by the mantle plume.
Bernhard Steinberger has calculated the movement and pressure that the super volcano near present-day Madagascar could cause further north on the Arabian Peninsula and in what is now the Mediterranean. He has also published a “kitchen table experiment” on Youtube, which illustrates the movements. Link: https:/
###
Original study:
Douwe J.J. van Hinsbergen, Bernhard Steinberger, Carl Guilmette, Marco Maffione, Derya Gürer, Kalijn Peters, Alexis Plunder, Peter McPhee, Carmen Gaina, Eldert L. Advokaat, Reinoud L.M. Vissers, Wim Spakman, “A record of plume-induced plate rotation triggering subduction initiation”, Nature Geoscience https:/
Contact details (not for publication)
Dr. Bernhard Steinberger
Scientist
GFZ Section Geodynamic Modelling
+49 331 288-1881
Stephan van Meulebrouck, press officer Faculty of Geosciences, Utrecht University, S.H.J.vanMeulebrouck@uu.nl, +31 6 2360 4383
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



