Main attraction: Scientists create world’s thinnest magnet
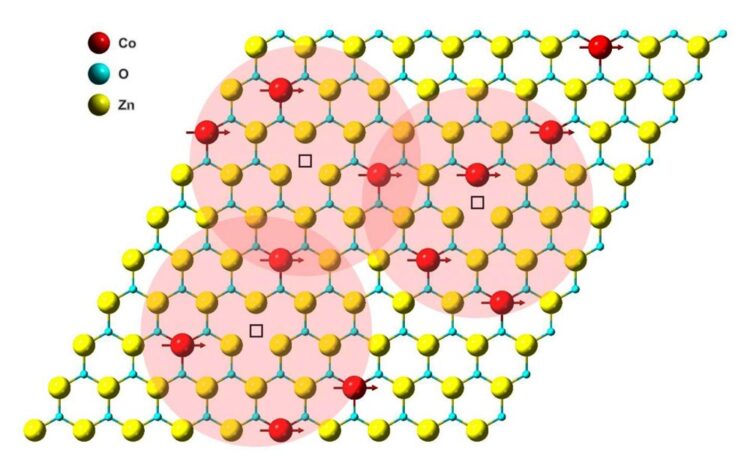
Illustration of magnetic coupling in a cobalt-doped zinc-oxide monolayer. Red, blue, and yellow spheres represent cobalt, oxygen, and zinc atoms, respectively.
Credit: Berkeley Lab
A one-atom thin 2D magnet could advance new applications in computing and electronics.
The development of an ultrathin magnet that operates at room temperature could lead to new applications in computing and electronics – such as high-density, compact spintronic memory devices – and new tools for the study of quantum physics.
The ultrathin magnet, which was recently reported in the journal Nature Communications , could make big advances in next-gen memories, computing, spintronics, and quantum physics. It was discovered by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley.
“We’re the first to make a room-temperature 2D magnet that is chemically stable under ambient conditions,” said senior author Jie Yao, a faculty scientist in Berkeley Lab’s Materials Sciences Division and associate professor of materials science and engineering at UC Berkeley.
“This discovery is exciting because it not only makes 2D magnetism possible at room temperature, but it also uncovers a new mechanism to realize 2D magnetic materials,” added Rui Chen, a UC Berkeley graduate student in the Yao Research Group and lead author on the study.”
The magnetic component of today’s memory devices is typically made of magnetic thin films. But at the atomic level, these magnetic films are still three-dimensional – hundreds or thousands of atoms thick. For decades, researchers have searched for ways to make thinner and smaller 2D magnets and thus enable data to be stored at a much higher density.
Previous achievements in the field of 2D magnetic materials have brought promising results. But these early 2D magnets lose their magnetism and become chemically unstable at room temperature.
“State-of-the-art 2D magnets need very low temperatures to function. But for practical reasons, a data center needs to run at room temperature,” Yao said. “Theoretically, we know that the smaller the magnet, the larger the disc’s potential data density. Our 2D magnet is not only the first that operates at room temperature or higher, but it is also the first magnet to reach the true 2D limit: It’s as thin as a single atom!”
The researchers say that their discovery will also enable new opportunities to study quantum physics. “Our atomically thin magnet offers an optimal platform for probing the quantum world,” Yao said. “It opens up every single atom for examination, which may reveal how quantum physics governs each single magnetic atom and the interactions between them. With a conventional bulk magnet where most of the magnetic atoms are deeply buried inside the material, such studies would be quite challenging to do.”
The making of a 2D magnet that can take the heat
The researchers synthesized the new 2D magnet – called a cobalt-doped van der Waals zinc-oxide magnet – from a solution of graphene oxide, zinc, and cobalt. Just a few hours of baking in a conventional lab oven transformed the mixture into a single atomic layer of zinc-oxide with a smattering of cobalt atoms sandwiched between layers of graphene. In a final step, graphene is burned away, leaving behind just a single atomic layer of cobalt-doped zinc-oxide.
“With our material, there are no major obstacles for industry to adopt our solution-based method,” said Yao. “It’s potentially scalable for mass production at lower costs.”
To confirm that the resulting 2D film is just one atom thick, Yao and his team conducted scanning electron microscopy experiments at Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Foundry to identify the material’s morphology, and transmission electron microscopy imaging to probe the material atom by atom.
With proof in hand that their 2D material really is just an atom thick, the researchers went on to the next challenge that had confounded researchers for years: Demonstrating a 2D magnet that successfully operates at room temperature.
X-ray experiments at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source characterized the 2D material’s magnetic parameters under high temperature. Additional X-ray experiments at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory’s Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource verified the electronic and crystal structures of the synthesized 2D magnets. And at Argonne National Laboratory’s Center for Nanoscale Materials, the researchers imaged the 2D material’s crystal structure and chemical composition using transmission electron microscopy.
As a whole, the research team’s lab experiments showed that the graphene-zinc-oxide system becomes weakly magnetic with a 5-6% concentration of cobalt atoms. Increasing the concentration of cobalt atoms to about 12% results in a very strong magnet.
To the researchers’ surprise, a concentration of cobalt atoms exceeding 15% shifts the 2D magnet into an exotic quantum state of “frustration,” whereby different magnetic states within the 2D system are in competition with each other.
And unlike previous 2D magnets, which lose their magnetism at room temperature or above, the researchers found that the new 2D magnet not only works at room temperature but also at 100 degrees Celsius (212 degrees Fahrenheit).
“Our 2D magnetic system shows a distinct mechanism compared to previous 2D magnets,” said Chen. “And we think this unique mechanism is due to the free electrons in zinc oxide.”
True north: Free electrons keep magnetic atoms on track
When you command your computer to save a file, that information is stored as a series of ones and zeroes in the computer’s magnetic memory, such as the magnetic hard drive or a flash memory. And like all magnets, magnetic memory devices contain microscopic magnets with two poles – north and south, the orientations of which follow the direction of an external magnetic field. Data is written or encoded when these tiny magnets are flipped to the desired directions.
According to Chen, zinc oxide’s free electrons could act as an intermediary that ensures the magnetic cobalt atoms in the new 2D device continue pointing in the same direction – and thus stay magnetic – even when the host, in this case the semiconductor zinc oxide, is a nonmagnetic material.
“Free electrons are constituents of electric currents. They move in the same direction to conduct electricity,” Yao added, comparing the movement of free electrons in metals and semiconductors to the flow of water molecules in a stream of water.
The researchers say that new material – which can be bent into almost any shape without breaking, and is 1 millionth the thickness of a single sheet of paper – could help advance the application of spin electronics or spintronics, a new technology that uses the orientation of an electron’s spin rather than its charge to encode data. “Our 2D magnet may enable the formation of ultra-compact spintronic devices to engineer the spins of the electrons,” Chen said.
“I believe that the discovery of this new, robust, truly two-dimensional magnet at room temperature is a genuine breakthrough by Jie Yao and his students,” said co-author Robert Birgeneau, a faculty senior scientist in Berkeley Lab’s Materials Sciences Division and professor of physics at UC Berkeley who co-led the study’s magnetic measurements. “In addition to its obvious significance to spintronic devices, this 2D magnet is fascinating at the atomic level, revealing for the first time how cobalt magnetic atoms interact over ‘long’ distances” through a complex two-dimensional network, he added.
“Our results are even better than what we expected, which is really exciting. Most of the time in science, experiments can be very challenging,” he said. “But when you finally realize something new, it’s always very fulfilling.”
###
Co-authors on the paper include researchers from Berkeley Lab, including Alpha N’Diaye and Padraic Shafer of the Advanced Light Source; UC Berkeley; UC Riverside; Argonne National Laboratory; and Nanjing University and the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China.
The Advanced Light Source and Molecular Foundry are DOE national user facilities at Berkeley Lab.
The Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource is a DOE national user facility at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.
The Center for Nanoscale Materials is a DOE national user facility at Argonne National Laboratory.
This work was funded by the DOE Office of Science, the Intel Corporation, and the Bakar Fellows Program at UC Berkeley.
Founded in 1931 on the belief that the biggest scientific challenges are best addressed by teams, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and its scientists have been recognized with 14 Nobel Prizes. Today, Berkeley Lab researchers develop sustainable energy and environmental solutions, create useful new materials, advance the frontiers of computing, and probe the mysteries of life, matter, and the universe. Scientists from around the world rely on the Lab’s facilities for their own discovery science. Berkeley Lab is a multiprogram national laboratory, managed by the University of California for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit energy.gov/science.
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


