Neutralizing the SARS-CoV-2 sugar coat
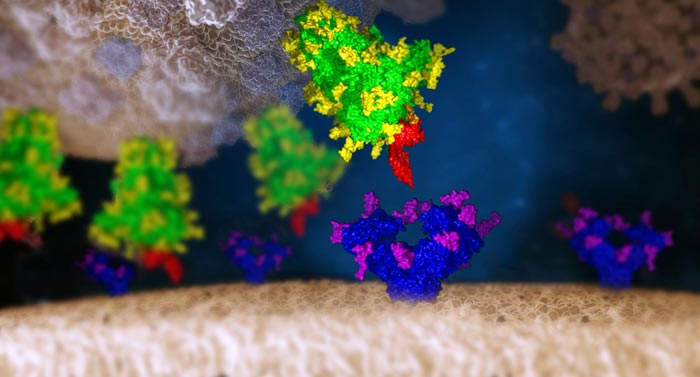
Das SARS-CoV-2-Virus interagiert mit einer menschlichen Zelle
©IMP/IMBA Graphics 2021. Die Protein- und Glykanstrukturen wurden von Chris Oostenbrink (BOKU) zur Verfügung gestellt.
Researchers identify two sugar-binding proteins that impede the viral entry of circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants. The team, spearheaded by researchers at IMBA – Institute of Molecular Biotechnology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences – may have found the “Achilles’ heel” of the virus, with potential for pan-variant therapeutic interventions. The findings are now published in the EMBO Journal.
Amidst the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, it is paramount to find new ways to contain the spread of SARS-CoV-2. To this end, the Spike (S) protein is of particular interest as it mediates the main entry mechanism of the virus into host cells. Thus, the interaction of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein with the host cells’ angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) determines the infectivity of the virus. The importance of the S protein for the survival and spread of the virus dictates the presence of a camouflage mechanism. Hence, the virus uses so-called glycosylation as a cloaking mechanism to form a sugar coat at specific sites of the Spike protein in order to hide from the host’s immune response.
Spotting the wolf by its sheep’s clothing
The reasoning might seem simple at first sight, but one obvious question immediately surfaced in the team around IMBA group leader Josef Penninger, who is also the director of the Life Sciences Institute at the University of British Columbia (UBC), Vancouver, Canada. Namely: what about the lectins, the sugar-binding proteins? “We intuitively thought that the lectins could help us find new interaction partners of the sugar-coated Spike protein,” says co-first author David Hoffmann, a former PhD student in the Penninger lab at IMBA. The attractivity of this question lies precisely in how spot on it is: the glycosylation sites of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein remain highly conserved among circulating variants. Thus, by identifying lectins that bind these glycosylation sites, the researchers could be well on their way to developing robust therapeutic interventions.
Indeed, the team developed and tested a library of over 140 mammalian lectins. Among these, two were found to strongly bind to the SARS-CoV-2 S protein: Clec4g and CD209c. “We now have tools at hand that can bind the virus’ protective layer and thereby block the virus from entering cells,” summarizes Stefan Mereiter, co-first author and postdoctoral researcher in the Penninger lab. Mereiter then exclaims: “This mechanism could indeed be the Achilles’ heel scientists have been longing to find!”
The road from SARS-CoV-2’s “immunity shield” or “sheep’s clothing” to its Achilles’ heel involved several state-of-the-art research techniques. In collaboration with Peter Hinterdorfer of the Institute of Biophysics at the University of Linz, Austria, the team used high-tech biophysical methods to analyze how the lectin binding takes place in detail. For example, the researchers measured which binding forces and how many bonds occur between the lectins and the Spike protein. This also made it clear to which sugar structures Clec4g and CD209c attach.
Therapeutic interventions on the horizon
More good news: the team found that the two lectins bind to the N-glycan site N343 of the Spike protein. This specific site is so crucial to the Spike that it can never be lost in any infectious variant. In fact, a deletion of this glycosylation site renders the Spike protein unstable. In addition, other groups have also shown that viruses with mutated N343 were non-infectious. “This means, that our lectins bind to a glycan site that is essential for Spike function – it is therefore very unlikely that a mutant could ever arise that lacks this glycan,” explains Mereiter.
And the story does not end here. To the team’s excitement, the two lectins also decreased SARS-CoV-2 infectivity of human lung cells. For Josef Penninger and the whole team, these findings hold promise for pan-variant therapeutic interventions against SARS-CoV-2.
Penninger sums up: “The approach compares to the mechanism of the drug candidate ‘APN01’ [Apeiron Biologics], which is undergoing advanced clinical trials. This is a bioengineered human ACE2 that also binds to the Spike protein. When the Spike protein is occupied by the drug, the gateway into the cell is blocked. Now, we identified naturally occurring, mammalian lectins that are capable of doing just that!”
The production of the recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein under controlled conditions was carried out at the Institute of Biochemistry of the University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences (BOKU), Vienna and coordinated by Prof. Lukas Mach as part of the BOKU Covid initiative. This production respected the precise localization of the conserved sugar chain that allow endogenous lectins to attach the virus. This highly specialized form of glycoprotein analysis has been the research focus of Friedrich Altmann’s group at BOKU for decades. “Although the analysis of the spike glycoprotein is already quite a considerable challenge under normal conditions, it was only possible to perform the necessary measurements in these special times of home-office, distance-learning and hard lock-downs due to the great teamwork of everyone. I would like to express my sincere thanks to all the people involved,” says Johannes Stadlmann, project lead in the Altmann research group at BOKU.
This work involved an international team of researchers including Ali Mirazimi at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden. In addition, several senior researchers in Austria contributed to this work: Johannes Stadlmann, Chris Oostenbrink, Lukas Mach and Friedrich Altmann at BOKU, Peter Hinterdorfer at the Johannes Kepler University Linz, as well as Gerald Wirnsberger at Apeiron Biologics, Vienna.
Original publication:
Hoffmann D., Mereiter, S. et al., “Identification of lectin receptors for conserved SARS-CoV-2 glycosylation sites”, EMBO J, 2021. DOI: 10.15252/embj.2021108375
https://www.embopress.org/doi/10.15252/embj.2021108375
About IMBA:
IMBA – Institute of Molecular Biotechnology – is one of the leading biomedical research institutes in Europe focusing on cutting-edge stem cell technologies, functional genomics, and RNA biology. IMBA is located at the Vienna BioCenter, the vibrant cluster of universities, research institutes and biotech companies in Austria. IMBA is a subsidiary of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, the leading national sponsor of non-university academic research. The stem cell and organoid research at IMBA is being funded by the Austrian Federal Ministry of Science and the City of Vienna.
Journal: The EMBO Journal
DOI: 10.15252/embj.2021108375
Article Title: Identification of lectin receptors for conserved SARS-CoV-2 glycosylation sites
Article Publication Date: 9-Aug-2021
Media Contact
Daniel Azar
daniel.azar@imba.oeaw.ac.at
Office: (0)1-79044
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



