A protein causes higher risk of severe cancer progression for men
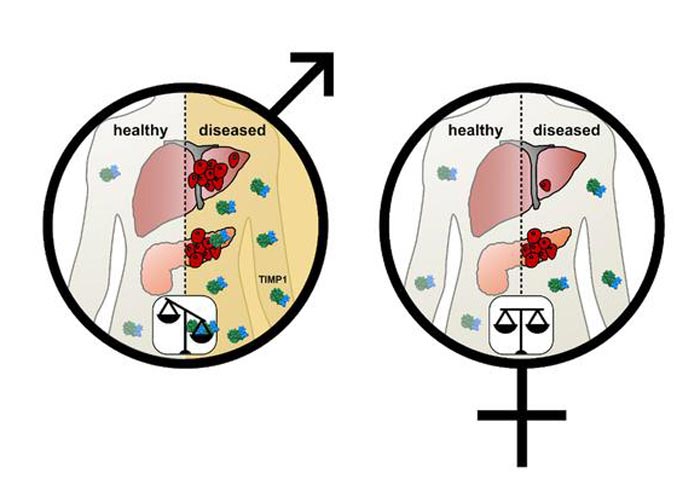
The difference in TIMP1 levels between the sexes: The male-specific increase of TIMP1 levels causes a significantly higher risk, both for metastasis of the tumor in the liver and for earlier death.
Credit: Hermann et al.
Originally published in Journal of Experimental Medicine
A remarkable number of life-threatening diseases manifest more severely in males than in females. One current example is COVID-19 caused by SARS CoV-2. Another example is the significantly higher risk of severe cancer progression for men. A research team at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has now discovered a molecular cause for this difference between sexes.
Compared to women, men have a higher risk of experiencing severe progression of life-threatening diseases such as cancer. For example in Germany, every year over 130,000 male patients die of cancer as compared to only 100,000 female patients. [According to the National Cancer Institute (USA) the cancer mortality rate in the US is 189.5 per 100,000 for men but only 135.7 per 100,000 for women.]
Comprehensive epidemiological studies conducted in recent years have shown that the increased risk of men experiencing a more severe course of cancer is not exclusively based on a higher-risk lifestyle, such as a higher average consumption of tobacco or alcohol.
Thus, life-style-independent factors have to play a role, making it all the more important to identify parameters which cause the sex-specific course of the disease. This in turn might serve as a basis for improving decision-making and approaches of treatment.
A protein is the cause
A research team led by Prof. Achim Krüger at TUM’s university hospital Klinikum rechts der Isar has now identified the protein TIMP1 as a factor, which could explain this sex-specific difference and also improve the risk-diagnostics for the clinical course of the disease. The work was funded by the Wilhelm Sander Foundation, among other sources.
Based on patient cohorts from Germany and Canada, the research team found that men, whose blood contained a higher concentration of the endogenous protein TIMP1 also have a significantly higher risk of dying from cancer.
Further analyses then showed that the increase in TIMP1 causes increased liver metastasis, resulting in death in cases of pancreatic cancer, colon cancer, and melanoma.
Increased values indicate higher risk
“TIMP1 is not higher in all males, but the discovery of TIMP1 as a risk parameter, which can be identified in blood, now allows clinicians to identify the very group of men exhibiting a higher risk of developing life-threatening liver metastases,” says Krüger.
“Previous studies have already shown the molecular context in which TIMP1 promotes liver metastasis,” he adds. “In connection with our current discovery, there are now new possibilities for personalized medicine with optimized diagnosis and targeted therapy options.”
In a next step Achim Krüger and his working group plan to further investigate the molecular causes of male-specific modifications in increased production of TIMP1 in the body.
The Wilhelm Sander Foundation, whose stated objective is the promotion of medical research, in particular of projects relating to the fight against cancer, supported the research project in two funding phases with a total of approximately 400,000 euros. In addition, the project received support from the German Research Foundation (DFG), die DZIF German Center for Infection Research, the Princess Margaret Cancer Foundation, the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO) and the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation.
In addition to several groups at the university hospital TUM Klinikum rechts der Isar, scientists of Toronto’s University Health Network Princess Margaret Cancer Centre and of the University of Toronto Department of Medical Biophysics were also involved in the research activities.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Prof. Dr. Achim Krüger
Technical University of Munich, Klinikum rechts der Isar
Institute of Molecular Immunology and Experimental Oncology
Ismaninger Str. 22, 81675 Munich, Germany
Tel.: +49 89 4140 4463 – E-Mail: achim.krueger@tum.de
Originalpublikation:
C. D. Hermann, B. Schoeps, C. Eckfeld, E. Munkhbaatar, L. Kniep, O. Prokopchuk, N. Wirges, K. Steiger, D. Häußler, P. Knolle, E. Poulton, R. Khokha, B. T. Grünwald, I. E. Demir, A. Krüger
TIMP1 expression underlies sex disparity in liver metastasis and survival in pancreatic cancer
J Exp Med., Nov 1, 2021; 218(11):e20210911 (Online: Sep 17, 2021) – DOI: 10.1084/jem.20210911
Weitere Informationen:
https://rupress.org/jem/article-abstract/218/11/e20210911/212647/TIMP1-expressio… Original publication
https://www.tum.de/en/about-tum/news/press-releases/details/36939 Press release at TUM-website
http://www.imi-muenchen.de/research-groups/krueger/research-group-krueger Website of the research group
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



