A new spin on MRI
University of Tsukuba researchers have demonstrated a proof-of-concept modification to enable standard MRI systems to detect frequencies associated with the presence of sodium-23 ions. This low-cost and convenient approach requires the installation of a radio-frequency repeater inside the magnetic bore of an MRI machine. The wide applicability of this method for sodium and other nuclei may allow advanced medical imaging to be performed on existing machines, and substantially reduce MRI scanner upgrade costs for hospitals.
Credit: University of Tsukuba
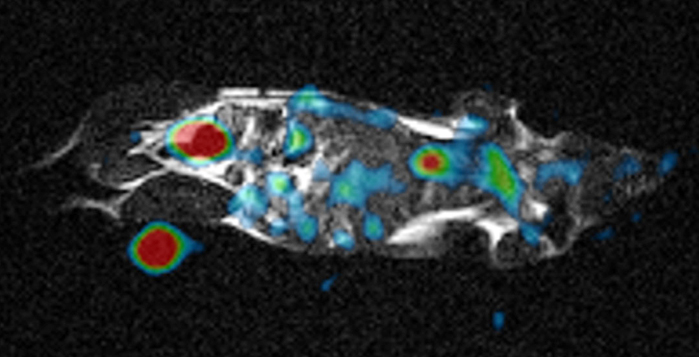
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba place a radio-frequency repeater inside an MRI machine that allows it to detect sodium ions, which may lead to enhanced clinical imaging and monitoring functionality at very low cost.
Scientists at the University of Tsukuba demonstrated how conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines can be retrofitted to detect sodium ions using a cross band radio-frequency repeater. This work may allow for new medical diagnostics to be performed without expensive new equipment.
Magnetic resonance imaging has become a crucial part of the medical toolkit for non-invasive visualization of internal organs. MRI machines operate by placing the patient in a very strong magnetic field, which will cause the nuclear spins of atoms in the body to align in the same direction, essentially acting like tiny magnets. Then, a radio-frequency (RF) signal of a very specific frequency is applied, which has the ability to flip the direction of the spins. When the nuclei relax back to their original aligned state, the precession of these spins about the magnet field direction can be measured by RF detector coils to determine the concentration of that particular atom. The majority of MRI machines in use today are optimized to look for the presence of hydrogen (1H) nuclei, which are naturally abundant in the body as a component of water molecules. Retrofitting such a machine for detecting other isotopes, like sodium-23 23Na, would require a great deal of expensive hardware upgrades.
Now, a team of researchers at the University of Tsukuba have demonstrated a proof-of-concept method for equipping a conventional MRI machine with the capability to image 23Na by installing a cross band RF repeater system. This is a device that receives signals at a certain frequency and rebroadcast at a different one. “The RF repeater, which is a commonly used device in amateur radio, can be placed directly inside the magnet bore of an existing MRI machine as a cost-effective upgrade,” explains author Professor Yasuhiko Terada. This allows the frequency produced by 23Na, which is around 17 MHz, to be detected by the coils tuned at the 64 MHz of MRI.
The research team tested the system with a saline “phantom” and an anesthetized mouse. Even though the resulting signal was much lower compared with custom-built 23Na machines, it could be amplified to produce comparable images. “Watching the motion of sodium ions inside the body provides detailed metabolic information not available from conventional MRI images,” Professor Terada says. 23Na imaging has already been shown to be useful for applications involving the kidney, owing to its large sodium concentration, as well as the brain and heart. This approach may substantially reduce health care costs by providing completely new abilities to existing machines without requiring a complete refurbishment.
The work is published in Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences as “Development of an add-on 23Na-MRI radiofrequency platform for a 1H-MRI system using a crossband repeater: proof-of-concept” (DOI:10.2463/mrms.tn.2021-0094).
Funding: This research was supported by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development AMED (Grant Number JP20hm0102062)
DOI: 10.2463/mrms.tn.2021-0094
Article Title: Development of an add-on 23Na-MRI radiofrequency platform for a 1H-MRI system using a crossband repeater: proof-of-concept
Media Contact
Naoko Yamashina
University of Tsukuba
kohositu@un.tsukuba.ac.jp
All latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



