Hostile takeover in the cell
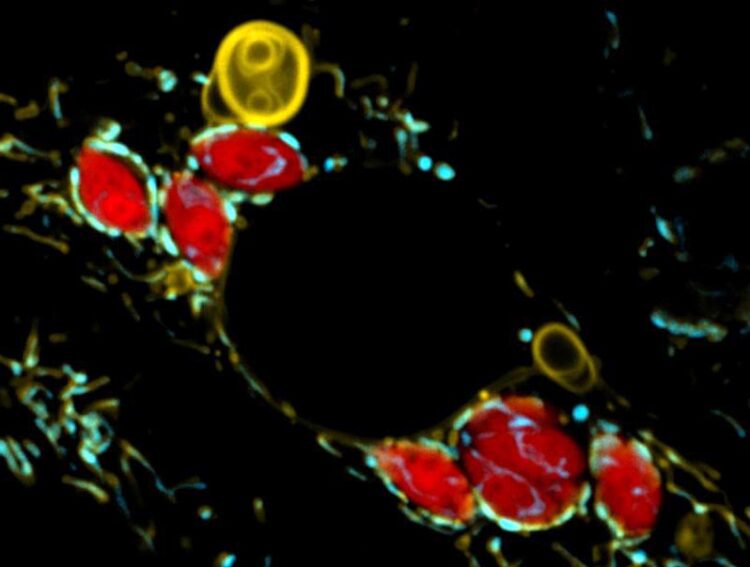
The parasite Toxoplasma gondii (red) causes mitochondria (green) to shed large structures of their "skin" (yellow).
Xianhe Li/Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing, 2022
Pathogens hijack host mitochondria.
Mitochondria are known as energy suppliers for our cells, but they also play an important role in the defense against pathogens. They can initiate immune responses, and deprive pathogens of the nutrients they need to grow. A research team led by Lena Pernas of the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing in Cologne, Germany, has now shown that pathogens can turn off mitochondrial defense mechanisms by hijacking a normal cellular response to stress.
To survive, pathogens need to acquire nutrients from their host and counter host defenses. One such defense comes from host mitochondria, which can deprive them of nutrients they need and thus restrict their growth. “We wanted to know how else mitochondrial behaviour changes when mitochondria and pathogens meet in cells. Because the outer membrane of these organelles is the first point of contact with the pathogens, we took a closer look at it,” explains Lena Pernas, research group leader at the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing.
Mitochondria shed their ´skin`
The researchers infected cells with the human parasite Toxoplasma gondii and observed live under the microscope what happens to the outer compartment of mitochondria. “We saw that mitochondria in contact with the parasite started shedding large structures from their outer membrane. This was so puzzling to us. Why would mitochondria shed what is essentially the gateway between them and the rest of the cell?” says Xianhe Li, first author of the study.
Hostile takeover
But how does the parasite get the mitochondria to do it? The research team was able to show that the pathogen has a protein that functionally mimics a host mitochondrial protein. It binds to a receptor on the outer membrane of mitochondria, to gain access to the machinery that ensures proteins are transported inside the mitochondria. “In doing so, the parasite hijacks a normal host response to mitochondrial stress that, in the context of infection, effectively disarms the mitochondria” Pernas said. “Other researchers have shown that a SARS-CoV-2 virus protein also binds to this transport receptor. This suggests the receptor plays an important role in the host-pathogen interaction. But further investigation is needed to better understand its role during different infections.”
Lena Pernas is also a group leader at the CECAD Cluster of Excellence in Aging Research at the University of Cologne.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Dr. Lena Pernas, 0221 379 70 770, LPernas@age.mpg.de
Originalpublikation:
Xianhe Li, Julian Straub, Tânia Catarina Medeiros, Chahat Mehra, Fabian den Brave, Esra Peker, Ilian Atanassov, Katharina Stillger, Jonas Benjamin Michaelis, Emma Burbridge, Colin Adrain, Christian Münch, Jan Riemer, Thomas Becker, Lena F. Pernas
Mitochondria shed their outer membrane in response to infection-induced stress
Science, Jan 14 2022
Weitere Informationen:
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



