Researchers simulate SARS-COV-2 transmission and infection on airline flights
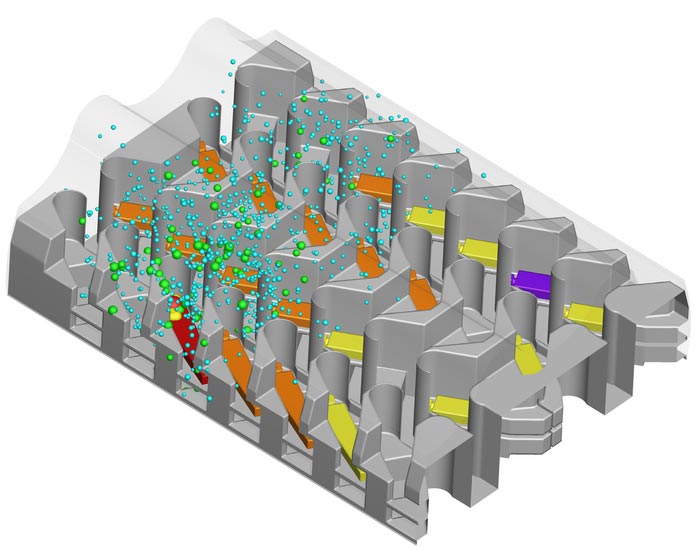
A study published in Indoor Air simulated the transmission of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, on a flight from London to Hanoi and on another flight from Singapore to Hangzhou.
Credit: Dr. Lai
A study published in Indoor Air simulated the transmission of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, on a flight from London to Hanoi and on another flight from Singapore to Hangzhou.
When simulating the dispersion of droplets of different sizes generated by coughing, talking, and breathing activities in an airline cabin by an infected person, researchers found that SARS-CoV-2 virus contained in such droplets traveled with the cabin air distribution and was inhaled by other passengers.
The scientists counted the number of viral copies inhaled by each passenger to determine infection. Their method correctly predicted 84% of the infected/uninfected cases on the first flight. The team also found that wearing masks and reducing conversation frequency between passengers could help to reduce the risk of exposure on the second flight.
“We are very pleased to see that our model validated by experimental data can achieve such a high accuracy in predicting COVID-19 transmission in airliner cabins,” said corresponding author Dayi Lai, PhD, Associate Professor and Associate Head of the Department of Architecture, School of Design of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, in China. “Also, it’s important to know that wearing masks makes a significant impact on reducing the transmission.”
All latest news from the category: Studies and Analyses
innovations-report maintains a wealth of in-depth studies and analyses from a variety of subject areas including business and finance, medicine and pharmacology, ecology and the environment, energy, communications and media, transportation, work, family and leisure.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



