The cellular cleaning program autophagy helps in wound healing
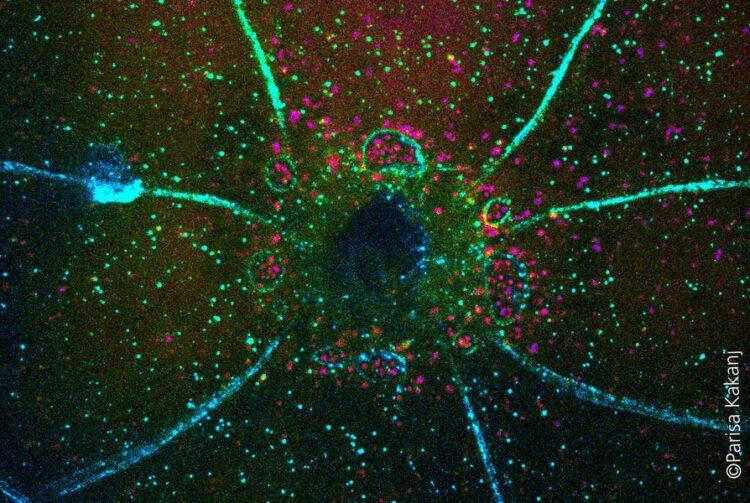
Closing of a wound in Drosophila larva. Membranes are marked in blue and autophagic vesicles in magenta.
(c) Parisa Kakanj
Scientists at the University of Cologne have shown that the recycling program of cells, autophagy, leads to the fusion of several single cells into multinucleated cell units during wound healing / publication in ‘The EMBO Journal’.
A team led by Professor Dr. Maria Leptin has shown in animal models that autophagy, a mechanism of stress responses in cells, plays an important role in wound healing: When a wound develops, the process of autophagy is initiated and regulated by the protein complex TORC1. This is a newly discovered function of autophagy and the first evidence that autophagy controls the formation of syncytia (multinucleated cells) outside the placenta or muscle development. There, the process had already been observed in the past. The article, ‘Autophagy-mediated plasma membrane removal promotes the formation of epithelial syncytia’ has been published in The EMBO Journal.
Autophagy is a cellular recycling system that has been conserved over the course of evolution from yeast to humans. Autophagic vesicles, small bubbles within the cell, recognize, engulf, and digest invaders such as bacteria and viruses or the cell’s own material such as accumulated protein clumps. The material is recycled, thus providing the cell with raw materials under stressful conditions. During aging, infection, or disease, when proper cellular function declines and harmful products accumulate in organs, autophagy function is instrumental in restoring health. In turn, dysfunction of autophagy increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, as well as cancer and infections.
In the new study, scientists from the CECAD Cluster of Excellence for Aging Research, the Center for Molecular Medicine Cologne (CMMC), and the Institute of Genetics (all at the University of Cologne) as well as the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg investigated the function of autophagy in wound healing and in the healthy and uninjured epidermis (skin) of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. In the process studied here, autophagy hence did not digest viruses or bacteria, but the cell’s own cell membrane, so that boundaries between cells broke down and a large cell with multiple nuclei was formed.
The team observed that autophagy is increased in the cells surrounding the wound. This leads to a selective breakdown of the membranes that connect the cells. Eventually, a large, multinucleated cell (syncytium) is formed. ‘When we genetically triggered autophagy in healthy, uninjured skin, we again observed the same phenomenon: the membrane between adjacent cells is lost and large patches of multinucleated syncytia form throughout the epidermis,’ said Parisa Kakanj, PhD, first author of the study. ‘It is surprising that the formation of syncytia, which we already know to occur in the formation of some organs such as muscles or placenta, also occurs in wound healing. The role of autophagy in this may also be important for our understanding of disease mechanisms, since multinuclear cells are also found in tumors and infected tissues.’
In previous studies of muscle and placenta development, the formation of a syncytium results in mechanical stability, provides a strong barrier function to protect tissue from pathogens, and enables the cell to digest larger pathogens or cellular debris. Whether the process performs similar functions in wound healing is not yet clear. This will be the subject of future studies.
The investigators also observed an interaction of the autophagic vesicles with the lateral plasma membrane of the cell in the healthy, unwounded epidermis as well as in the cells surrounding the wound. In this context, proper function of the TORC1 protein complex, which has a central regulatory function in cell metabolism, and here also controls autophagy, is crucial to prevent destruction of the epidermis by autophagy. Based on these and other observations, the team hypothesizes that the lateral plasma membrane is a potential source of the autophagic vesicles. ‘Autophagy is a double-edged sword, the precise extent and spatiotemporal activity of which determines whether it is useful or problematic,’ said Professor Maria Leptin. In order to be able to use the beneficial side of autophagy for prevention and therapy, it is even more important to understand how autophagy is activated and how autophagic vesicles are formed.
Media Contact:
Dr. Parisa Kakanj
Institute for Genetics
+49 221 470 3528
pkakanj@uni-koeln.de
Professorin Dr. Maria Leptin
Institute for Genetics
+49 221 470 3401
mleptin@uni-koeln.de
Press and Communications Team:
Dr. Anna Euteneuer
+49 221 478 84043
anna.euteneuer@uni-koeln.de
Publication:
https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.15252/embj.2021109992
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



