Artificial cell membrane channels composed of DNA
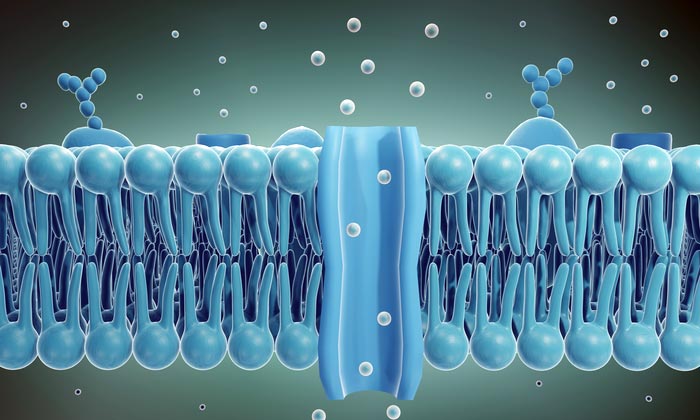
Graphic shows the bilayer structure of a living cell membrane, composed of phospholipid. A phospholipid consists of a hydrophilic or water-loving head and hydrophobic or water-fearing tail. The hydrophobic tails are sandwiched between two layers of hydrophilic heads. At the center, a channel is shown, permitting the transport of biomolecules. The new study describes a process for creating artificial channels using segments of DNA that insert into cell membranes and allow the reversible transit of various cargo, including ions and proteins.
Credit: Biodesign Institute at ASU
… can be opened and locked with a key.
Technique opens new possibilities for smart drug delivery and other applications.
Just as countries import a vast array of consumer goods across national borders, so living cells are engaged in a lively import-export business. Their ports of entry are sophisticated transport channels embedded in a cell’s protective membrane. Regulating what kinds of cargo can pass through the borderlands formed by the cell’s two-layer membrane is essential for proper functioning and survival.
In new research, Arizona State University professor Hao Yan, along with ASU colleagues and international collaborators from University College London describe the design and construction of artificial membrane channels, engineered using short segments of DNA. The DNA constructions behave much in the manner of natural cell channels or pores, offering selective transport of ions, proteins, and other cargo, with enhanced features unavailable in their naturally occurring counterparts.
These innovative DNA nanochannels may one day be applied in diverse scientific domains, ranging from biosensing and drug delivery applications to the creation of artificial cell networks capable of autonomously capturing, concentrating, storing, and delivering microscopic cargo.
“Many biological pores and channels are reversibility gated to allow ions or molecules to pass through,” Yan says. Here we emulate these nature processes to engineer DNA nanopores that can be locked and opened in response to external “key” or “lock” molecules.”
Professor Yan is the Milton D. Glick Distinguished Professor in Chemistry and Biochemistry at ASU and directs the Biodesign Center for Molecular Design and Biomimetics. He is also a professor with ASU’s School of Molecular Sciences.
The research findings appear in the current issue of the journal Nature Communications.
All living cells are enveloped in a unique biological structure, the cell membrane. The science-y term for such membranes is phospholipid bilayer, meaning the membrane is formed from phosphate molecules attached to a fat or lipid component to form an outer and inner membrane layer, (see figure 1).
These inner and outer membrane layers are a bit like a room’s inner and outer walls. But unlike normal walls, the space between inner and outer surfaces is fluid, resembling a sea. Further, cell membranes are said to be semipermeable, allowing designated cargo entry or exit from the cell. Such transport typically occurs when the transiting cargo binds with another molecule, altering the dynamics of the channel structure to permit entry into the cell, somewhat like the opening of the Panama Canal.
Semipermeable cell membranes are necessary for protecting sensitive ingredients within the cell from a hostile environment outside, while allowing the transit of ions, nutrients, proteins and other vital biomolecules.
Researchers, including Yan, have explored the possibility of creating selective membrane channels synthetically, using a technique known as DNA nanotechnology. The basic idea is simple. The double strands of DNA that form the genetic blueprint for all living organisms are held together through the base pairing of the molecule’s 4 nucleotides, labelled A, T, C and G. A simple rule applies, namely that A nucleotides always pair with T and C with G. Thus, a DNA segment ATTCTCG would form a complimentary strand with CAAGAGC.
Base pairing of DNA allows the synthetic construction of a virtually limitless array or 2- and 3-D nanostructures. Once a structure has been carefully designed, usually with the aid of computer, the DNA segments can be mixed together and will self-assemble in solution into the desired form.
Creating a semipermeable channel using DNA nanotechnology, however, has proven a vexing challenge. Conventional techniques have failed to replicate the structure and capacities of nature-made membrane channels and synthetic DNA nanopores generally permit only one-way transport of cargo.
The new study describes an innovative method, allowing researchers to design and construct a synthetic membrane channel whose pore size permits the transport of larger cargo than natural cell channels can. Unlike previous efforts to create DNA nanopores affixed to membranes, the new technique builds the channel structure step-by-step, by assembling the component DNA segments horizontally with respect to the membrane, rather than vertically. The method permits the construction of nanopores with wider openings, allowing the transport of a greater range of biomolecules.
Further, the DNA design allows the channel to be selectively opened and closed by means of a hinged lid, equipped with a lock and key mechanism. The “keys” consist of sequence-specific DNA strands that bind with the channel’s lid and trigger it to open or close.
In a series of experiments, the researchers demonstrate the ability of the DNA channel to successfully transport cargo of varying sizes, ranging from tiny dye molecules to folded protein structures, some larger than the pore dimensions of natural membrane channels.
The researchers used atomic force microscopy and transmission electron microscopy to visualize the resulting structures, confirming that they conformed to the original design specifications of the nanostructures.
Fluorescent dye molecules were used to verify that the DNA channels successfully pierced and inserted themselves through the cell’s lipid bilayer, successfully providing selective entry of transport molecules. The transport operation was carried out within 1 hour of channel formation, a significant improvement over previous DNA nanopores, which typically require 5-8 hours for complete biomolecule transit.
The DNA nanochannels may be used to capture and study proteins and closely examine their interactions with the biomolecules they bind with or study the rapid and complex folding and unfolding of proteins. Such channels could also be used to exert fine-grained control over biomolecules entering cells, offering a new window on targeted drug delivery. Many other possible applications are likely to arise from the newfound ability to custom design artificial, self-assembling transport channels.
Journal: Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28522-2
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Cells
Article Title: A reversibly gated protein-transporting membrane channel made of DNA
Article Publication Date: 28-Apr-2022
Media Contact
Richard Harth
The Biodesign Institute at Arizona State University
Richard.Harth@asu.edu
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



