Fragile balance in the gut
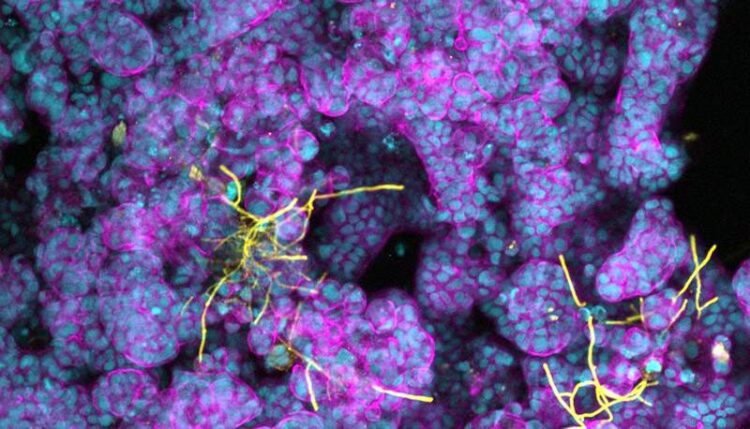
Candida albicans (yellow) forming hyphae on differentiated intestinal epithelial cells (nuclei in blue and F-actin in purple).
Credit: Raquel Alonso Roman / Leibniz-HKI
Intestinal cells and lactic acid bacteria work together against Candida infection.
The presence of probiotics such as lactic acid bacteria changes the environment in the intestine and forces the yeast fungus Candida albicans to change its metabolism, making it less infectious. This way, probiotics can contain or prevent the spread of fungal infections in the gut. Researchers at the Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology – Hans Knöll Institute (Leibniz-HKI) have also found that intestinal cells actively promote bacterial growth to protect themselves from the fungus. The findings were published in Nature Communications.
The yeast Candida albicans naturally colonizes the human body, especially common in the intestine. Usually this is a benign colonization, as the immune system and a healthy gut microbiome keep it in check. However, if the microbiome gets out of balance or the immune system is severely compromised, C. albicans can enter the bloodstream. This can be life-threatening especially for immunocompromised people in intensive care units.
Researchers at Leibniz-HKI have now found that human intestinal cells play an important role in fighting fungal infections caused by C. albicans. “The intestinal cells nourish lactic acid bacteria, which thereby multiply and in turn take nutrients away from the yeast fungus,” explains first author Raquel Alonso-Roman. The new conditions force C. albicans to adapt its metabolism, causing it to shed certain characteristics and making it less infectious. Adding the probiotics to the gut creates a balance between yeast, lactic acid bacteria and the rest of the microbiome, which restores a healthy state.
Infections with C. albicans, such as vulvovaginal infections, are already successfully treated with lactic acid bacteria. “We already know that lactic acid bacteria in particular can counteract a fungal infection, prevent it or even kill the fungus. Our work now addresses the question of ‘how’,” explains Bernhard Hube, head of the Department of Microbial Pathogenicity Mechanisms.
In collaboration with systems biologists at the institute, the researchers developed computer models that can predict how lactic acid bacteria of the species Lactobacillus rhamnosus behave when encountering C. albicans. “Using data from previous studies, our computer models can predict that the lactic acid bacteria would multiply and eventually counteract C. albicans,” explains Mark Gresnigt, junior group leader at Leibniz-HKI. However, subsequent experiments in the lab showed that the bacteria did not multiply in conventional culture media as predicted. “Only when we added epithelial cells from the gut did the lactic acid bacteria begin to multiply,” Gresnigt continued. Together with the junior research group of Slavena Vylkova, also at Leibniz-HKI, the researchers were able to find out how the yeast fungus changes its metabolism to adapt to the new conditions. Since there are no longer enough nutrients in the intestine, there is an adjustment in the gene activity of C. albicans, which makes the yeast fungus less infectious and thus no longer able to damage the intestinal cells.
The results of this research form an important step forward in the fight against life-threatening fungal infections. “We want to find out how probiotics fight infection. With this knowledge, we may be able to develop measures to prevent the aggressive behavior of the fungus. The idea is to influence the fungus the way probiotics would, without actually using them,” Hube explains. Especially in immunosuppressed patients, he said, it is usually too dangerous to use live bacteria as a remedy.
The balance and dysbalance of microorganisms in humans, animals and the environment are the central research focus of the Balance of the Microverse Cluster of Excellence and the Collaborative Research Center FungiNet, which supported this work.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Prof. Dr. Bernhard Hube
Microbial Pathgenicity Mechanisms – Leibniz-HKI
bernhard.hube@leibniz-hki.de
Originalpublikation:
Alonso-Roman R, Last A, Mirhakkak MH, Sprague JL, Möller L, Großmann P, Graf K, Gratz R, Mogavero S, Vylkova S, Panagiotou G, Schäuble S, Hube B, Gresnigt MS (2022) Lactobacillus rhamnosus colonisation antagonizes Candida albicans by forcing metabolic adaptations that compromise pathogenicity. Nature Communications, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30661-5
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



