Unveiling the mysteries of the genome structure in the human cell nucleus
New modeling technique provides a platform to investigate the relationship between the structure, dynamics, and functions of the human genome
Credit: Shin Fujishiro, Masaki Sasai
… using a 3D computational simulation.
A team of researchers at Nagoya University in Japan has created a 3-Dimensional computational simulation of the process of genome structure formation in the human cell nucleus. They expect the model to contribute to the understanding of cellular regulatory mechanisms and diseases, such as cancer, that damage the genome.
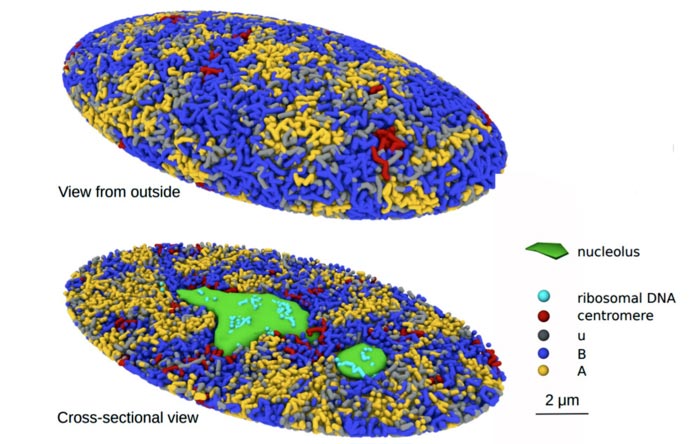
The three-dimensional structure of the genome plays a vital role in regulating the DNA functions of animal and plant cells because it affects its reading and replication. Shin Fujishiro and Masaki Sasai, Professor Emeritus of Nagoya University’s Department of Complex Systems Science, Graduate School of Informatics, constructed a 3D model by analyzing the whole genome of human cells. They used this model as a platform to investigate the relationship between the structure, dynamics, and functions of the human genome. The results were reported in the online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
“The spatial organization of DNA and its dynamic movement in cells are crucial for understanding cell functions,” Professor Sasai explains. “Researchers have devoted considerable effort to explaining DNA organization in cells by developing various experimental methods, including biochemical and microscope technologies, but now a unified picture is required. Our research introduces the first computational model that can quantitatively analyze various data from the full genome of human cells in a consolidated way.”
To help understand the process, the researchers investigated chromatin. Chromatin is a mixture of DNA with proteins that exist in cells as a way to keep the DNA compact. According to their model, chromatin is unevenly distributed and during the unfolding process that occurs during cell division, repulsive forces among the chromatin chains induce them to separate. This same force also separates chromatin into active and inactive compartments in the nuclei. The researchers found that their proposed mechanism clarified biochemical and microscopic findings of previous studies.
Professor Sasai adds: “Our model provides an indispensable tool and an original perspective in cell biology. From the computational model developed in this research, we can determine how perturbations in cells affect genome dynamics and organization. We can also investigate how disease cells, including various cancer cells, affect the genome. It allows us to more deeply analyze the relationship between genome structure and transcription regulation. The model developed in this research provides a fundamental tool and a new viewpoint in cell biology.”
This research was supported by the Japan Science and Technology Agency, Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST) (JPMJCR15G2), RIKEN Pioneering Project, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas “Chromatin Potential” (19H05258, 21H00248), Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas “Information Physics of Life” ( 20H05530), Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas B (19H01860), and Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas A (22H00406) supported by the Nagoya University Research Fund.
Journal: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.21098381
Article Title: Generation of dynamic three-dimensional genome structure through phase separation of chromatin
Media Contact
Matthew Coslett
Nagoya University
kouho-en@adm.nagoya-u.ac.jp
Office: 052-747-6862
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



