A gentler, more precise laser cutting technique
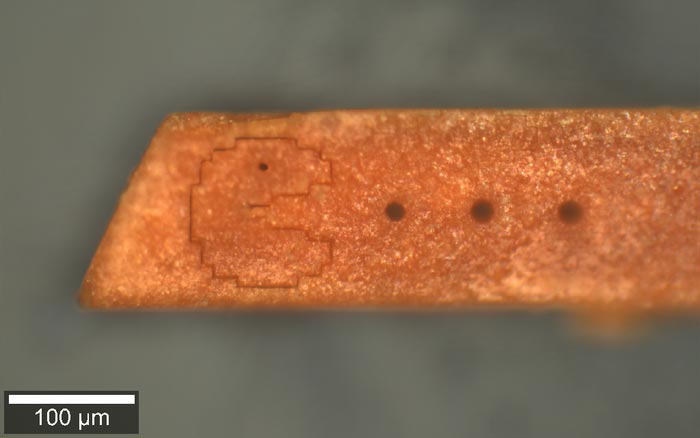
Pac-Man carving by laser cutting
Credit: H. Borchers et al.
Scientists from McGill University have developed a gentler, more precise technique using low-power visible light.
Laser cutting techniques are usually powered by high energy beams, so hot that they melt most materials. Now scientists from McGill University have developed a gentler, more precise technique using low-power visible light.
The new process called ‘cold photo-carving’ uses a fraction of the energy required in traditional laser cutting techniques. “We engineered crystal building blocks that can be cut by low-power light with amazing precision. Unlike traditional heat cutting methods, sculpting down to a resolution of nanometres is possible with our approach because light can be focused more precisely than heat can,” says Professor Tomislav Friščić of the Department of Chemistry.
According to the researchers, the new technique could also be used to engrave complex patterns into surfaces. “Imagine taking the famous geoglyphs in the Nazca Desert in Peru and engraving that pattern at a million-times the reduced size,” say Professor Friščić. The researchers hope that the new approach could one day be developed to create new materials like metals or ceramics that are easily shaped or cut using low-power light and are now looking at potential applications in solar cell materials.
“Cold photo-carving of halogen-bonded co-crystals of a dye and a volatile co-former using visible light” by T. H. Borchers et al. was published in Nature Chemistry.
Media Contact
Shirley Cardenas
McGill University
shirley.cardenas@mcgill.ca
Office: 514-398-6751
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



