Testosterone is an ally of macrophages in the battle against adrenal cancers
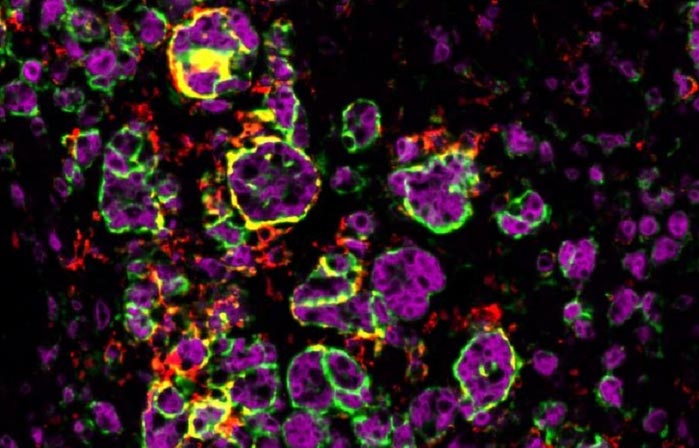
Macrophages attacking adrenal tumour in male mouse.
Credit: © Julie Olabe CNRS/GReD
Why are cancers of the adrenal glands1 more common among women? Why are prognoses worse for them? A team of scientists led by a CNRS researcher answers these questions in an article published on 14 October 2022 in Science Advances. They demonstrate that, in male mice, there is greater recruitment of immune cells known as macrophages, which can eliminate tumour cells.
Hence, aggressive tumour progression is scarcely seen in male mice; while in female miles, macrophages do not slow the growth of tumours, which eventually metastasize. Through molecular analyses, the team determined that recruitment of tumour-fighting macrophages depends on testosterone. After simple administration of the hormone to females, macrophages able to eradicate tumour cells were rallied to battle.
On the basis of these findings, the scientists conducted another study using data on humans, which revealed the same difference in macrophage recruitment rates between men and women with adrenal cancers. This discovery suggests the potential of hormonal stimulation as a treatment for this type of cancer, whose five-year survival rate is less than 30%.
1Le corps humain compte deux glandes surrénales, chacune située au-dessus d’un rein. Elles secrètent des hormones telles que l’adrénaline (participant, entres autres, au contrôle de la tension artérielle, de la fréquence cardiaque ou de la transpiration), des corticoïdes (impliqués dans le contrôle de la tension artérielle, des taux de sel et de potassium dans l’organisme et du métabolisme des sucres et des graisses), et des androgènes.
Journal: Science Advances
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.add0422
Article Title: Sexually dimorphic activation of innate antitumour immunity prevents adrenocortical carcinoma development
Article Publication Date: 14-Oct-2022
Media Contact
Priscilla Dacher
CNRS
presse@cnrs-dir.fr
Office: 0033-066-488-5277
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

A ‘language’ for ML models to predict nanopore properties
A large number of 2D materials like graphene can have nanopores – small holes formed by missing atoms through which foreign substances can pass. The properties of these nanopores dictate many…

Clinically validated, wearable ultrasound patch
… for continuous blood pressure monitoring. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new and improved wearable ultrasound patch for continuous and noninvasive…

A new puzzle piece for string theory research
Dr. Ksenia Fedosova from the Cluster of Excellence Mathematics Münster, along with an international research team, has proven a conjecture in string theory that physicists had proposed regarding certain equations….



