Colour-changing fibres for smart clothes
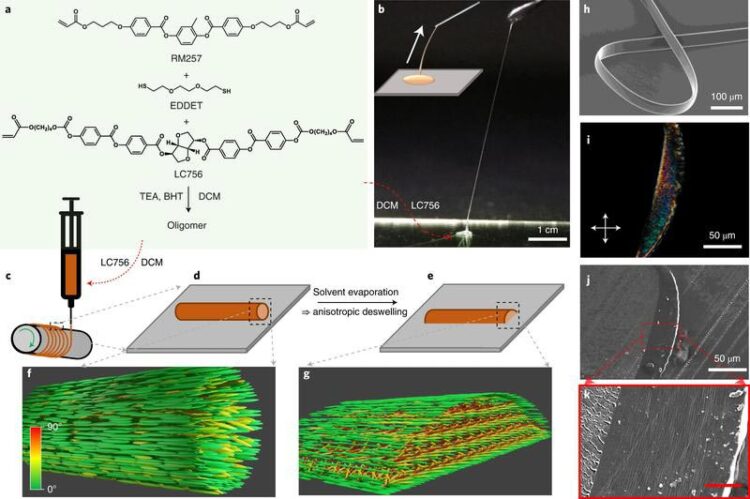
CLCE fibre production from oligomeric precursor liquid
(c) Geng, Kizhakidathazhath, Lagerwall / Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
What if the cloth changes its visual appearance when you stretch your hand?… such mechanoresponsive material has enormous potential in a large range of transformative applications in the beauty and health industry.
Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Elastomer (CLCE) is a structurally coloured polymer system capable of changing its colour by mechanical deformation, due to the coupling of colour of helically aligned liquid crystal molecules and the viscoelasticity of rubber. Prof. Jan Lagerwall, Dr. Yong Geng and Rijeesh Kizhakidathazhath at the University of Luxembourg created colour-changing CLCE fibres that can be easily sewn into the fabric.
The team at the Faculty of Science, Technology and Medicine developed a simple and scalable method to pull out fibres from CLCE precursor solution by adjusting the viscoelasticity of the solution. The colour of the fibres shifts continuously and reversibly from red to blue upon stretching.
Then, the researchers demonstrate the robustness of the CLCE fibres in garments by subjecting it to repeated stretching, machine washing and abrasion. The fibres remain colourful and mechanoresponsive. Such robust and colour-changing fibres open up numerous applications in wearable technology and other areas benefiting from autonomous strain sensing or detection of critically strong deformations.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Prof. Jan Lagerwall https://wwwen.uni.lu/research/fstm/dphyms/people/jan_lagerwall
Originalpublikation:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-022-01355-6
Weitere Informationen:
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



