Blind spots in the monitoring of plastic waste
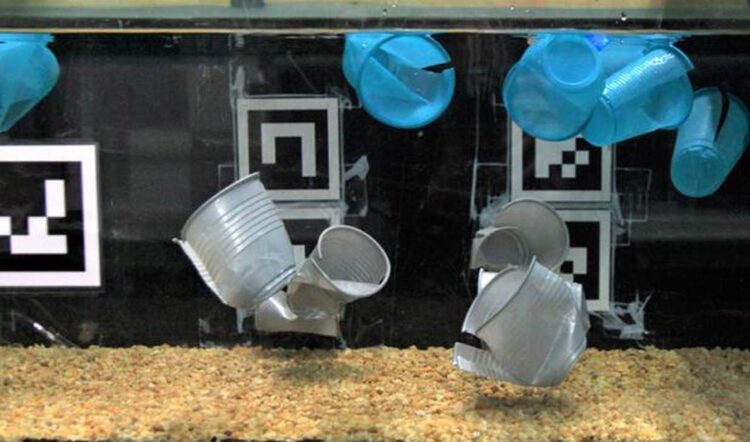
For their study, the researchers used river models that were filled with plastic waste (Photo: Daniel Valero / KIT)
KIT researchers and partners suspect that much more plastic is transported in flowing waters than previously assumed and are developing new modelling approaches.
Rivers play a key role in the transport of plastic in the environment. “As soon as plastic enters a river, it is transported rapidly and can spread throughout the environment,” says Dr Daniel Valero from the Institute of Water and River Basin Management at KIT and lead author of a new study on plastic transport. “But, depending on its size and material, plastic can behave very differently in the process. It can sink, be suspended in the water, remain afloat or be stopped by obstacles.” Current methods for estimating plastic pollution in rivers, however, are mainly based on surface observations. “This is the only way to effectively monitor large rivers from bridges. However, what happens under the water surface has not been sufficiently verified so far,” says Valero.
Plastic particles are transported very differently
Together with his research partners, Valero now investigated the behaviour of over 3,000 particles in the size range from 30 millimetres to larger objects such as plastic cups in flowing waters. In laboratory models, each individual particle was tracked in 3D with millimetre precision using a multi-camera system, whereby the entire water column – from the water surface to the bottom – was recorded. With this experiment, the researchers were able to statistically prove that plastic particles behave very differently depending on exactly where they are located in a river. Plastic that is transported below the water surface behaves as predicted by common models for turbulent flows. “The particles are dispersed like dust in the wind” says Valero. As soon as plastic emerges the water surface, however, the situation changes radically: “On contact with the water surface, the particles are caught by the surface tension like flies in a spider’s web. Then they cannot escape easily.” This adhesive effect is just as relevant for surface transport in rivers as the specific buoyancy of a plastic particle.
Better models for visual monitoring
On the one hand, the results of the experiment show that it is not enough to consider only floating plastic on the surface to estimate the amount of plastic in rivers. “The bias is significant. If the turbulent character of the transport of plastic particles under the water surface is not considered, then the amount of plastic waste in rivers can be underestimated by up to 90 percent,” says Daniel Valero. On the other hand, the results confirm that existing knowledge about the behaviour of particles in turbulent flows is relevant for the transport of plastic in rivers and that it can help to estimate the total amount more realistically. To this end, the researchers have quantified the ratio between concentrations of plastic particles at the water surface and at greater depths with different transport conditions. On this basis, monitoring can still be carried out by visual observation of the water surface and the actual transported quantity can be calculated relatively accurately. In addition, the results can help in a very practical way, namely in the development of new approaches for plastic removal: “If you can estimate where the most plastic is, then you also know where a clean-up is most effective,” says Valero. (mhe)
Original publication
Daniel Valero, Biruk S. Belay, Antonio Moreno-Rodenas, Matthias Kramer, Mário J. Franca: The key role of surface tension in the transport and quantification of plastic pollution in rivers. Water Research, 2022. DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.119078
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.119078
More information: https://www.klima-umwelt.kit.edu
Being “The Research University in the Helmholtz Association”, KIT creates and imparts knowledge for the society and the environment. It is the objective to make significant contributions to the global challenges in the fields of energy, mobility, and information. For this, about 9,800 employees cooperate in a broad range of disciplines in natural sciences, engineering sciences, economics, and the humanities and social sciences. KIT prepares its 22,300 students for responsible tasks in society, industry, and science by offering research-based study programs. Innovation efforts at KIT build a bridge between important scientific findings and their application for the benefit of society, economic prosperity, and the preservation of our natural basis of life. KIT is one of the German universities of excellence.
Journal: Water Research
DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.119078
Method of Research: Experimental study
Article Title: The key role of surface tension in the transport and quantification of plastic pollution in rivers
Article Publication Date: 28-Oct-2022
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Ecology, The Environment and Conservation
This complex theme deals primarily with interactions between organisms and the environmental factors that impact them, but to a greater extent between individual inanimate environmental factors.
innovations-report offers informative reports and articles on topics such as climate protection, landscape conservation, ecological systems, wildlife and nature parks and ecosystem efficiency and balance.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



