Decoding light-matter interactions on sub-nanometer scales
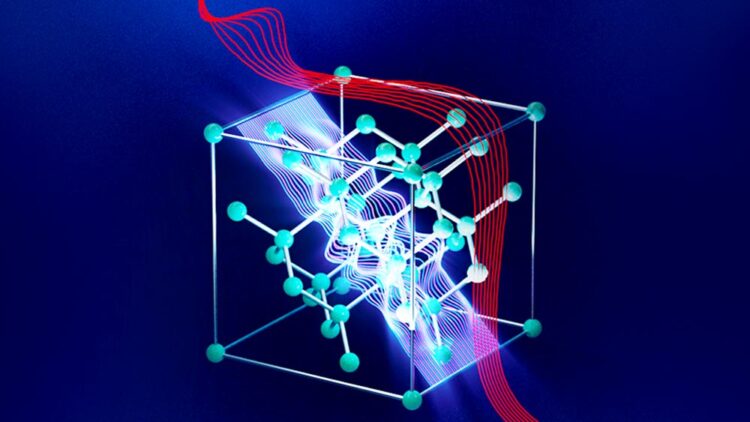
The figure above demonstrates picophotonics in the 3D lattice of silicon atoms. The red wave represents the conventional electromagnetic wave propagating in the solid. The blue inner wave represents the new predicted picophotonic wave. Graphic provided by Dr. Zubin Jacob / Purdue University
… leading to ‘picophotonics’.
Researchers at Purdue University have discovered new waves with picometer-scale spatial variations of electromagnetic fields which can propagate in semiconductors like silicon. The research team, led by Dr. Zubin Jacob, Elmore Associate Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Department of Physics and Astronomy (courtesy), published their findings in APS Physics Review Applied in a paper titled, “Picophotonics: Anomalous Atomistic Waves in Silicon.”
“The word microscopic has its origins in the length scale of a micron which is a million times smaller than a meter. Our work is for light matter interaction within the picoscopic regime which is far smaller, where the discrete arrangement of atomic lattices changes light’s properties in surprising ways,” says Jacob.
These intriguing findings demonstrate that natural media host a variety of rich light-matter interaction phenomena at the atomistic level. The use of picophotonic waves in semiconducting materials may lead researchers to design new, functional optical devices, allowing for applications in quantum technologies.
Light-matter interaction in materials is central to several photonic devices from lasers to detectors. Over the past decade, nanophotonics, the study of how light flows on the nanometer scale in engineered structures such as photonic crystals and metamaterials have led to important advances. This existing research can be captured within the realm of classical theory of atomic matter. The current finding leading to picophotonics was made possible by a major leap forward using a quantum theory of atomistic response in matter. The team consists of Jacob as well as Dr. Sathwik Bharadwaj, research scientist at Purdue University, and Dr. Todd Van Mechelen, former post-doc at Purdue University.
The long-standing puzzle in the field was the missing link between atomic lattices, their symmetries and the role it plays on deeply picoscopic light fields. To answer this puzzle, the theory team developed a Maxwell Hamiltonian framework of matter combined with a quantum theory of light induced response in materials.
“This is a pivotal shift from the classical treatment of light flow applied in nanophotonics,” says Jacob. “The quantum nature of light’s behavior in materials is the key for the emergence of picophotonics phenomena.”
Bharadwaj and colleagues showed that hidden amidst traditional well-known electromagnetic waves, new anomalous waves emerge in the atomic lattice. These light waves are highly oscillatory even within one fundamental building block of the silicon crystal (sub-nanometer length scale).
“Natural materials itself have rich intrinsic crystal lattice symmetries and light is strongly influenced by these symmetries,” says Bharadwaj. “The immediate next goal is to apply our theory to the plethora of quantum and topological materials and also verify the existence of these new waves experimentally.”
“Our group has been leading the frontier of research on pico-scale electrodynamic fields inside matter at the atomistic level,” says Jacob. “We recently initiated the picoelectrodynamics theory network where we are bringing together diverse researchers to explore macroscopic phenomena stemming from microscopic pico-electrodynamic fields inside matter.”
This research was funded by the DARPA QUEST program.
Writer: Cheryl Pierce, communications specialist, Earth, Atmospheric, Planetary Sciences | Physics/Astronomy, Purdue University
Journal: Physical Review Applied
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.18.044065
Article Title: Picophotonics: Anomalous Atomistic Waves in Silicon
Article Publication Date: 27-Oct-2022
Media Contact
Kayla Wiles
Purdue University
wiles5@purdue.edu
Office: 765-494-2432 x2432
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…


