HIV Dementia Mechanism Discovered
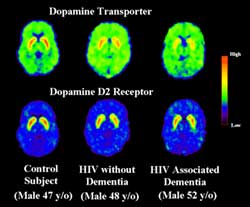
PET scans showing dopamine transporters (top row) and dopamine D2 receptors (bottom row) in a 47-year-old control subject (left), a 48-year-old HIV subject without dementia (middle), and a 52-year-old HIV subject with dementia (right), at the level of the basal ganglia. The images are scaled with respect to the maximum value obtained in the control subject and presented using the rainbow scale (red color - high value, violet low value). The HIV subjects with dementia showed significantly lower dopamine transporter availability bilaterally compared to the seronegative controls in the putamen and in the ventral striatum, but only mild and non-significant decreases in the caudate. The non-demented HIV patients, however, showed no significant decreases in dopamine transporters in the basal ganglia. Dopamine D2 receptor availability did not differ between the HIV and the control subjects in any of the regions.
Finding may lead to new therapies
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered a key mechanism in the brains of people with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) dementia. The study is the first to document decreases in the neurotransmitter dopamine in those with the condition, and may lead to new, more effective therapies. HIV dementia is a type of cognitive decline that is more common in the later stages of HIV infection.
“Our results offer the first evidence of dopamine terminal injury — specifically injury to dopamine transporters — in HIV dementia patients,” says Brookhaven physician Gene-Jack Wang, the study’s lead author. “This suggests that a decrease in transporters may contribute to the disease process. We believe our findings also indicate a new direction for treatment.” The study appears in the September 2004 issue of the British scientific journal Brain. Physician Linda Chang, formerly a researcher at Brookhaven Lab and now with the University of Hawaii, initiated this research.
“This study clearly demonstrates that HIV infection damages dopamine-associated brain cells, and provides a pathway for developing more effective treatments,” says National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Director Nora Volkow, co-investigator, who worked on the study while at Brookhaven Lab.
Using positron emission tomography (PET), a brain-scanning technique, Wang and colleagues looked at the brains of 15 HIV-positive study volunteers, some of whom had symptoms of dementia, and 13 HIV-negative volunteers. The purpose of the scans was to determine the presence of dopamine transporters and dopamine receptors.
Dopamine transporters, found on the terminals of some brain cells (neurons), recycle dopamine, a brain chemical that sends signals between the cells. Dopamine receptors are “docking ports” on the receiving neurons. Dopamine is associated with pleasure and reward and is also essential for movement; low levels are found in conditions such as Parkinson’s disease. Decreased dopamine transporters represent neuron damage and lower levels of functional dopamine neurons, as well as decreases in the release of dopamine.
Prior to brain scanning, each volunteer was given an injection containing a radiotracer, a radioactive chemical “tag” designed to “light up” activated areas of the brain. The PET camera picks up the radioactive signal and measures the level and location of the tracer. Two hours after the first scan, each volunteer was given a second radiotracer, and his/her brain was scanned again. The first scan looked specifically for the presence of dopamine receptors, and the second searched for dopamine transporters.
The researchers found that HIV-positive patients with, but not those without dementia, had significantly lower dopamine transporter levels in the putamen and ventral striatum, the brain regions containing the most transporters, compared with HIV-negative volunteers. Higher levels of HIV virus correlated with lower transporter levels in the caudate — part of the striatum — and in the putamen. Dopamine receptor levels showed only mild decreases in HIV-positive volunteers.
“These findings suggest that HIV patients with dementia may benefit from dopamine-enhancing treatments, especially those patients with more severe cognitive motor deficits,” says Wang. “Studies have shown, however, that some of these agents may actually exacerbate HIV-induced neurotoxicity, but antioxidants may block this mechanism. Further studies should focus on adjunctive approaches combining drugs in both classes.”
“Viral suppression seems to correlate with less injury to the dopamine system,” Wang continues. “Because of this correlation, future studies should look at whether viral suppression after antiretroviral treatment can lead to recovery of deficits in the dopamine system.”
This study was funded by the Office of Biological and Environmental Research within the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science and the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). All research was conducted at Brookhaven Lab; scientists now at NIDA, the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, and the University of Hawaii contributed to the study.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.bnl.govAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Humans vs Machines—Who’s Better at Recognizing Speech?
Are humans or machines better at recognizing speech? A new study shows that in noisy conditions, current automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems achieve remarkable accuracy and sometimes even surpass human…

Not Lost in Translation: AI Increases Sign Language Recognition Accuracy
Additional data can help differentiate subtle gestures, hand positions, facial expressions The Complexity of Sign Languages Sign languages have been developed by nations around the world to fit the local…

Breaking the Ice: Glacier Melting Alters Arctic Fjord Ecosystems
The regions of the Arctic are particularly vulnerable to climate change. However, there is a lack of comprehensive scientific information about the environmental changes there. Researchers from the Helmholtz Center…



