Laser against biofouling
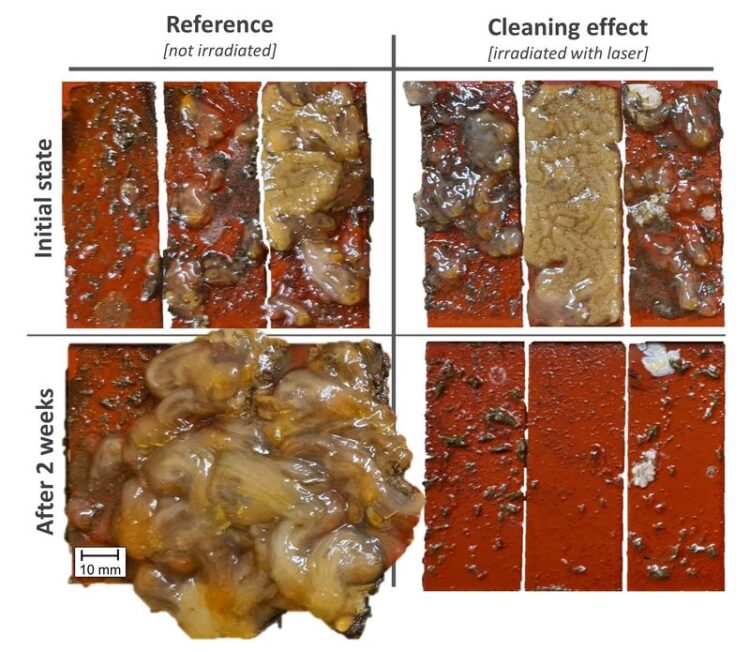
Results of the samples irradiated with the laser and those not irradiated.
Photo: LZH
Eco-friendly underwater cleaning of ship hulls.
The settlement of mussels and algae on ship hulls not only increases the fuel consumption of ships but can also threaten ecosystems. The Laser Zentrum Hannover e.V. (LZH) and partners have now developed a laser process to clean ship hulls underwater.
Photo: LZH
Biofouling is the growth of algae, mussels, and other marine organisms on the hull of a ship. The fouling increases the flow resistance of the ship – and thus increases fuel consumption and CO2 emissions. Mechanical cleaning of the fouling can damage the hull coating. In addition, the fouling must be extracted if organisms or even parts of the ship’s coating are not to get into the water. Scientists from the LZH, together with Laserline GmbH and the Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Applied Materials Research IFAM, have now developed an environmentally friendly and efficient solution to the problem of biofouling.
Eco-friendly cleaning with the laser underwater
Laser radiation can be used to lethally damage marine fouling underwater without damaging the underlying coating of the ship’s hull. The LZH scientists have developed a process in which the cells of the fouling are damaged by laser radiation in such a way that the fouling dies and is then simply washed away by the water after some time.
The researchers conducted their investigations in the south harbor of the island of Helgoland. There, they irradiated fouling samples with the laser, then returned them to the North Sea and checked them after two to four weeks. “We were able to achieve a clear, time-delayed cleaning effect,” says underwater technology expert Dr.-Ing. Benjamin Emde from the LZH. “With simulated currents, as would be added in real life with a moving ship, the cleaning effect is further enhanced.”
Reducing emissions and avoiding species displacement
Biofouling is not only a problem for reasons of fuel consumption as well as emissions. The fouling can lead to the introduction and spread of non-native species in foreign ecosystems. “Species displacement is a major risk of biofouling,” Emde says. If a ship introduces foreign organisms into an ecosystem through hull fouling, it can severely disrupt the ecosystem. In practice, this leads to ships being banned from docking in foreign ports, as has happened again recently with cruise ships, for example. Here, as well, cleaning with the laser is a good alternative to mechanical methods: Because the introduced biomass is lethally damaged during laser cleaning, it is no longer dangerous for foreign ecosystems afterward.
About FoulLas
The project “Fouling removal of maritime surfaces using laser radiation underwater – FoulLas” was carried out by the Laserline GmbH, the Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials IFAM and the Laser Zentrum Hannover e.V. (LZH). The project was funded by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK) under the funding code 03SX489 by the project coordinator Jülich.
Weitere Informationen:
https://www.lzh.de/en/press-releases/2023/laser-against-biofouling-eco-friendly-…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Ecology, The Environment and Conservation
This complex theme deals primarily with interactions between organisms and the environmental factors that impact them, but to a greater extent between individual inanimate environmental factors.
innovations-report offers informative reports and articles on topics such as climate protection, landscape conservation, ecological systems, wildlife and nature parks and ecosystem efficiency and balance.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



