Structural insights illuminate the arms race between crop plants and fungal pathogens
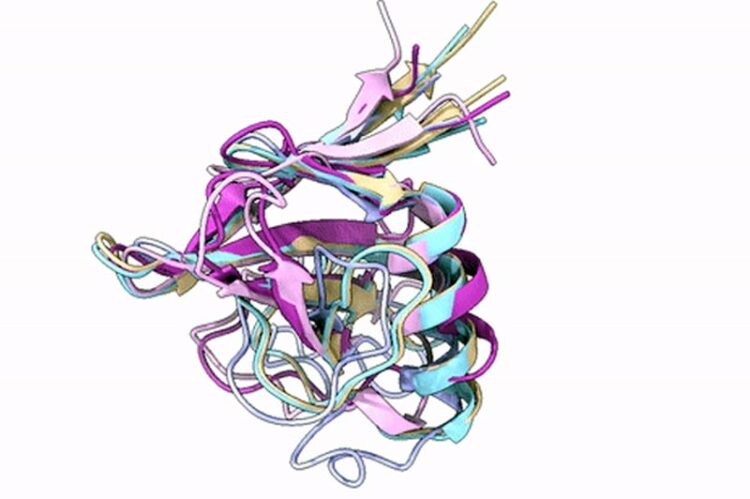
Superposition of the five Blumeria graminis AVR effector crystal structures.
(c) Yu Cao
Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research shed light on how harmful fungi evade recognition by their plant hosts and aid infection.
Many cereal crops, such as wheat and barley, are prey to devastating fungal diseases caused by infection with so-called grass powdery mildews. A key battleground between the plants and the powdery mildews is the interaction between plant immune receptors and pathogen effectors, molecules which are delivered into host cells by pathogens to establish infection. These effectors and immune receptors are locked in a molecular arms race in which the fungus needs to continuously adapt its effector repertoire to avoid recognition by adapted immune receptors and maintain virulence activity.
However, the structures and functions of these numerous effectors – which can run into the hundreds for individual fungal lineages – remain incompletely characterized.
Now, scientists from Germany, Switzerland and China led by Paul Schulze-Lefert, director at the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research in Cologne and Jijie Chai who holds positions at Westlake University, Hangzhou and Tsinghua University, both in China, have reported the structures of several powdery mildew effectors from different subfamilies.
These structures show how effectors adopt a common structural scaffold with some local variations that allow them to evade recognition by immune receptors. Their findings are published in the journal PNAS.
Using X-ray crystallography, a technique that allows scientists to deduce the positions of atoms in a molecule based on electron density, first authors Yu Cao and Florian Kümmel and colleagues acquired structures for five different effectors from two different powdery mildews that infect barley and wheat. Strikingly, although the similarity between the effectors was very low at the level of DNA sequence, they were all found to adopt a common structural fold, known as RALPH after RNase-like proteins associated with haustoria.
Analysis of these structures revealed that they are indeed similar to that of RNase proteins, enzymes that bind to, and break down RNA molecules. Intriguingly, however, these effectors do not possess any RNase activity. Instead, the authors suggest that this common fold RALPH framework may be important for critical processes related to infection, such as assembly into functional effectors and the ability to cross biological membranes. The local structural changes in the RALPH scaffold may explain why the effectors can associate with different host proteins to allow infection.
Armed with an understanding of the structural template of a RALPH effector, the researchers then set out to determine whether they could engineer recognition between immune receptors and effectors in instances where effector divergence had led to immune escape. Strikingly, they found that six amino acid substitutions were sufficient to turn a sequence-diverged effector into one that was recognized by a specific immune receptor. Analysis of further effector-receptor pairs allowed the authors to conclude that each immune receptor detects largely distinct patches on the surface of its corresponding effector.
“It is one of the eureka moments of science when, in evolution, the molecular arms race between plants and pathogens can be explained by local structural changes within a shared three-dimensional protein architecture”, says Paul Schulze-Lefert.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Paul Schulze-Lefert
+49 221 5062 350
schlef@mpipz.mpg.de
Originalpublikation:
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



