Molecular manganese complex as superphotooxidant
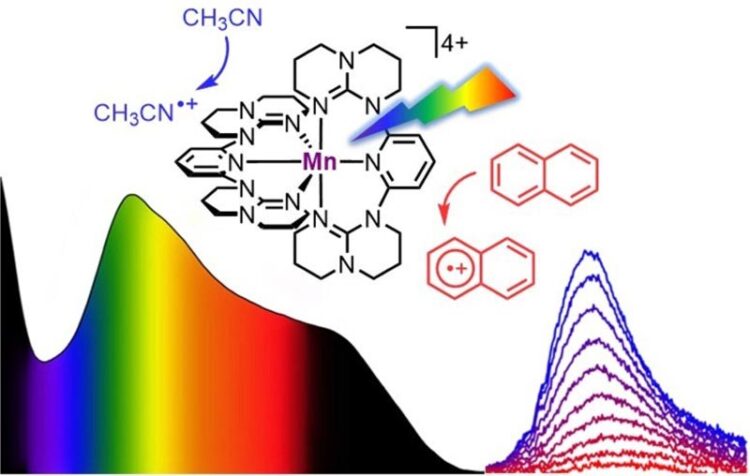
Challenging photooxidations using the "molecular Braunstein" and light
Credit: ill./©: Katja Heinze / JGU
Scientists developed a new molecular system made from the abundant element manganese for photooxidations.
Highly reducing or oxidizing photocatalysts are a fundamental challenge in photochemistry. Only a few transition metal complexes with Earth-abundant metal ions have so far advanced to excited state oxidants, including chromium, iron, and cobalt. All these photocatalysts require high energy light for excitation and their oxidizing power has not yet been fully exploited. Furthermore, precious and hence expensive metals are the decisive ingredients in most cases. A team of researchers headed by Professor Katja Heinze of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) has now developed a new molecular system based on the element manganese. Manganese, as opposed to precious metals, is the third most abundant metal after iron and titanium and hence widely available and very cheap.
Unusual behavior of “molecular Braunstein”
The team of Professor Katja Heinze has designed a soluble manganese complex that absorbs all visible light from blue to red, i.e., in a wavelength of 400 to 700 nanometers, and parts of the near-infrared light up to 850 nanometers. This panchromatic absorption of the complex is reminiscent of the dark color of Braunstein or manganese dioxide, which is a natural mineral. In contrast to the mineral Braunstein, the new “molecular Braunstein” emits NIR-II light with a wavelength of 1,435 nanometers after excitation with visible or NIR-I light with a wavelength of 850 nanometers. “This is an unusual observation for a molecular system based on manganese in its oxidation state +IV. Even with noble metals emission in this energy region is essentially unprecedented,” said Professor Katja Heinze.
Even more intriguing beyond this NIR-II luminescence from a molecular manganese system is the observation that after photoexcitation the “molecular Braunstein” can oxidize various organic substrates. This includes extremely challenging aromatic molecules with very high oxidation potentials such as naphthalene, toluene, or benzene. “Even otherwise very stable solvents can be attacked by the superphotooxidant when excited by LED light”, emphasized Dr. Nathan East, who prepared the new complex and performed all photolysis experiments during his PhD in the group of Professor Katja Heinze.
Observation of two photoactive states thanks to ultrafast spectroscopy
Ultrafast spectroscopic techniques using laser pulses with sub-picosecond time resolution revealed an unusual excited-state reactivity and two different photoactive states: a very short-lived but extremely oxidizing high-energy state and a longer-lived moderately oxidizing lower-energy state. The former can attack solvent molecules that are already close to complex before the light excitation, while the latter excited state exists long enough to attack aromatic substrates after diffusional collision. “This is called static and dynamic quenching of the excited states”, explained Dr. Robert Naumann, a senior scientist specialized in time-resolved spectroscopy in the group of Professor Katja Heinze.
Quantum chemical calculations to understand unusual photoprocesses
“A detailed picture of the photoinduced processes emerged when we modeled the involved excited states by quantum chemical calculations in the light of the spectroscopic results”, added Heinze. “These advanced and time-consuming calculations were only possible using the computing power of the supercomputers MOGON and ELWETRITSCH in Rhineland-Palatinate,” said Dr. Christoph Förster, a senior scientist in the group of Katja Heinze, who was strongly involved in the quantum chemical study.
In the future, scientists may be able to develop new challenging light-driven reactions using the common and abundant metal manganese. This will not only replace the rare, more costly ruthenium and iridium compounds, which today are still the most frequently used, but even enable reaction and substrate classes that are unavailable with the classical compounds. “With our own newly installed ultrafast laser system, the computing power of high-performance supercomputers, and the creativity and skills of our PhD students we will continue to push on with our efforts to develop a more sustainable photochemistry”, emphasized Professor Katja Heinze.
Research as part of the Light Controlled Reactivity of Metal Complexes priority program funded by the German Research Foundation
The group’s results have been published in Nature Chemistry. The German Research Foundation (DFG) and the Max Planck Graduate Center with Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (MPGC) are funding this research. In 2018, the German Research Foundation set up the priority program Light Controlled Reactivity of Metal Complexes (SPP 2102), coordinated by Professor Katja Heinze with the second funding period having started in 2022.
Related links:
- https://www.ak-heinze.chemie.uni-mainz.de/ – Research group of Professor Dr. Katja Heinze at the JGU Department of Chemistry
- https://www.spp2102.uni-mainz.de/ – DFG Priority Program 2102: Light Controlled Reactivity of Metal Complexes (SPP 2102)
- https://susinnoscience.uni-mainz.de/ – JGU Top-level Research Area SusInnoScience: Sustainable Chemistry as the Key to Innovation in Resource-efficient Science in the Anthropocene
- https://www.mpgc-mainz.de/ – Max Planck Graduate Center with Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (MPGC)
Journal: Nature Chemistry
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-024-01446-8
Article Title: Oxidative two-state photoreactivity of a manganese(IV) complex using near-infrared light
Article Publication Date: 8-Feb-2024
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



