Physics of complex fluids
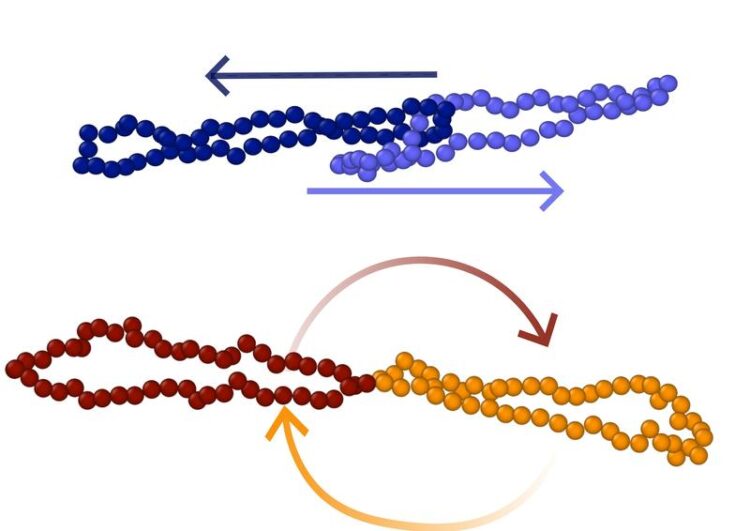
Schematic of poly[2]catenane slip tumbling and bonded ring gradient tumbling.
Credit: Reyhaneh A. Farimani
Ring polymers show unexpected motion patterns under shear.
It all depends on the linking: How ring polymers move…
An international research team is attracting the attention of experts in the field with computational results on the behavior of ring polymers under shear forces: Reyhaneh Farimani, University of Vienna, and her colleagues showed that for the simplest case of connected ring pairs, the type of linkage – chemically bonded vs. mechanically linked – has profound effects on the dynamic properties under continuous shear. In these cases novel rheological patterns emerge. In addition to being recently published in the prestigious journal Physical Review Letters, the study received an “Editors’ Suggestion” for its particular novelty.
The shearing of fluids – meaning the sliding of fluid layers over each other under shear forces – is an important concept in nature and in rheology, the science that studies the flow behavior of matter, including liquids and soft solids. Shear forces are lateral forces applied parallel to a material, inducing deformation or slippage between its layers. Fluid shear experiments allow the characterization of important rheological properties such as viscosity (resistance to deformation or flow) and thixotropy (decrease in viscosity under the influence of shear) which are important in applications ranging from industrial processes to medicine. Studies on the shear behavior of viscoelastic fluids, created by introducing polymers into Newtonian fluids, have already been conducted in recent years. However, a novel approach in the current research involves the consideration of polymer topology – the spatial arrangement and structure of molecules – by using ring polymers. Ring polymers are macromolecules composed of repeating units, forming closed loops without free ends.
A Matter of Linking
First author Reyhaneh Farimani explains: “For our computer simulation experiments under shear, we considered two similar types of connected ring pairs: One in which the linkage is chemical, called bonded rings (BRs), and one in which the linkage is mechanical via a Hopf link, called polycatenanes (PCs).” Special emphasis was placed on taking into account hydrodynamic interactions through appropriate simulation techniques, which proved to be crucial since the emerging patterns are governed by a delicate interplay between fluctuating hydrodynamics and topology. The results were surprising: On the one hand, the response of the two components, BRs and PCs, was very different from each other – and on the other hand, it was clearly different from that of various other polymer types, such as linear, star or branched. In particular, the dominant dynamic pattern in other polymers under shear (“vorticity tumbling”) is either suppressed (BRs) or virtually absent (PCs) in these topologically modified polymers.
Unexpected Types of Tumbling
“What we discovered,” says Christos Likos, co-author of the study, “are completely unexpected dynamic patterns in both ring polymer types, which we call gradient-tumbling and slip-tumbling.” Due to an interplay between hydrodynamics and ring topology, the BR molecules tumble around the gradient direction, which is perpendicular to the vorticity and flow axes. BRs are found to be in a continuous gradient-tumbling motion under shear. On the contrary, PCs become thin, orient themselves close to the flow axis and maintain a fixed, stretched and non-tumbling conformation under shear. Instead, due to their peculiar form of mechanical linkage, PCs exhibit intermittent dynamics, with occasional exchange of the two rings as they slip through each other, a pattern the authors of the paper call slip-tumbling.
These unexpected modes of motion, which bear unique signatures of the topologies of the polymer compounds, underscore the importance of the interplay between hydrodynamics and polymer architecture: In fact, the researchers found in their simulations that when the backflow effects are artificially eliminated, the differences between BRs and PCs disappear. These dynamical modes also have a noticeable effect on the mechanical properties of the solution, since BRs release internal stresses by tumbling, whereas PCs store stresses permanently, resulting in a much higher viscosity in the latter case. This leads to the hypothesis that the different tumbling motions and structures of PCs and BRs could influence the shear viscosity – a fluid’s resistance to flow under shear reflecting its internal friction and ability to deform – of highly concentrated solutions or polymer melts of these molecules. Further experimental and theoretical studies are needed to test this hypothesis. The current study was conducted by a scientific cooperation between the University of Vienna, the Sharif University of Technology in Iran and the International School of Advanced Studies (SISSA) in Italy.
Original publication in Physical Review Letters:
Effects of linking topology on the shear response of connected ring polymers: Catenanes and bonded rings flow differently. Reyhaneh A. Farimani, Zahra Ahmadian Dehaghani, Christos N. Likos, and Mohammad Reza Ejtehadi
https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.148101
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



