Scientists develop first satellite deforestation tracker for whole of Latin America
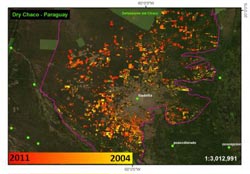
This shows deforestation around the dry Chaco of Paraguay from 2004-2011. Credit: www.terra-i.org/Karolina Argote/Louis Reymondin<br>
An international team of researchers in Colombia, the UK, USA and Switzerland have developed the first ever system to monitor deforestation across Latin America in near real-time using satellite data. Preliminary results from the new system reveal that in parts of Colombia, deforestation has increased by 340 per cent since 2004; and over a million hectares of forest have been lost in the Gran Chaco region of Paraguay.
The new satellite system, known as Terra-i, is being launched this week in time for the Rio+20 UN environment conference, and is soon to be expanded to cover all tropical regions. Although Brazil has had a sophisticated near real-time deforestation monitoring system in place since 2008, until now there has been no equivalent for the rest of Latin America.
Terra-i has been developed to monitor changes land cover every 16 days and for every 250 metres on the ground, in order to help national governments, conservation organisations and those implementing climate-related policy to assess recent trends in deforestation and emerging hotspots of change. The system uses data supplied by NASA's MODIS satellite sensor and is the result of collaboration between the International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT) in Colombia, The Nature Conservancy (TNC) in the USA and South America, the School of Engineering and Management of Vaud (HEIG-VD) in Switzerland and King's College London.
Deforestation can lead to widespread loss of biodiversity and also impacts the 'ecosystem services' that foster a stable climate and secure freshwater supplies. However, in many parts of the world the scale and pattern of deforestation is infrequently and inconsistently monitored and this makes management of change very difficult.
Huge volumes of data need to be processed to detect land cover change at a 250m spatial resolution every 16 days. Moreover, separating real human-induced changes, such as deforestation, from changes brought about by natural seasonality and by droughts, floods or persistent cloud cover, has made the development of an operational monitoring system a real challenge. The availability of MODIS imagery means that assessment of land cover change can be made in a geographically consistent manner between countries and also updated frequently.
The development of the Terra-i system was led Louis Reymondin, PhD student in the Department of Geography at King's College London, supervised by Dr Mark Mulligan, in collaboration with CIAT and HEIG-VD and funded by TNC.
'We developed a computational neural network and 'trained' it with data from 2000-2004 to recognise the normal changes in vegetation greenness due to seasonal variation in rainfall in different areas,' said Dr Mulligan, who is attending the Rio+20 conference this week.
'The network now recognises where and when greenness suddenly changes well beyond these normal limits as a result of deforestation. The system runs on data for every 250 square metres of land from Mexico to Argentina shortly after the data comes in from MODIS and highlights every 16 days the pixels that significantly change, writing these results to Google Maps for easy visualisation,' he said.
Preliminary data from Terra-i show that in Caquetá, Colombia for example, deforestation grew from around 4,880 hectares in 2004 to 21,440 in 2011, up by 340 per cent. Deforestation has grown significantly in the buffer zones of the Chiribiquete National Park where deforestation rates increased by 196 per cent from 2010 to 2011.
The Gran Chaco in Paraguay is the second largest forested area in South America. Terra-i found that between 2004 and 2010, over a million hectares of this area was deforested with a peak in 2009 of 454,700 hectares.
'As we approach Rio+20 in which the world will define the targets that will guide us along the road to a more sustainable development, it is critical that we deploy the appropriate tools to carefully monitor and manage our landscapes,' said Dr Mulligan.
'We need to ensure that we maintain enough farmland to feed the nine billion to come but we must also have protected natural landscapes that provide clean water, a stable climate, a refuge for biodiversity and space for increasingly urbanised populations to experience and appreciate the wonders of nature.
'Achieving the right balance between intelligently intensive agriculture and protected natural environments across the world will be fundamental to achieving truly sustainable development and requires sophisticated, geographically detailed and timely tools such as Terra-i to support appropriate policy and decision-making'.
CONTACT
Katherine Barnes
International Press Officer
King's College London
Tel: +44 207 848 3076
Email: Katherine.barnes@kcl.ac.uk
Notes to editors
Terra-i has a range of applications, such as monitoring the effectiveness of conservation, assessing the contribution of deforestation to climate change and understanding the likely impacts of deforestation on downstream and downhill populations. Results reported by Terra-i have also been connected to web-based hydrological models to help understand the impacts of recent deforestation on water resources, flooding and sedimentation of downstream areas.
Terra-i can be viewed at: http://maps.terra-i.org/
Visualisation using Google Maps at: http://geodata.policysupport.org/terra-i
Images available on request
Credits for all images: http://www.terra-i.org/Karolina Argote/Louis Reymondin
1) Chiribiquete National Park.tif
Map of deforestation around the Chiribiquete National Park, Colombia from 2004-2011
2) Dry-Chaco.tif
Deforestation around the dry Chaco of Paraguay from 2004-2011
3) Para.tif
Deforestation in and around protected areas in Para, Brazil from 2004-2011
For further information about The Nature Conservancy (TNC) visit: http://www.nature.org/
For further information about CIAT Colombia visit: http://www.ciat.cgiar.org
For further information about HEIG-VD, Switzerland visit: http://www.heig-vd.ch/
About King's College London (http://www.kcl.ac.uk)
King's College London is one of the top 30 universities in the world (2011/12 QS international world rankings), and was The Sunday Times 'University of the Year 2010/11', and the fourth oldest in England. A research-led university based in the heart of London, King's has nearly 23,500 students (of whom more than 9,000 are graduate students) from nearly 140 countries, and some 6,000 employees. King's is in the second phase of a £1 billion redevelopment programme which is transforming its estate.
King's has an outstanding reputation for providing world-class teaching and cutting-edge research. In the 2008 Research Assessment Exercise for British universities, 23 departments were ranked in the top quartile of British universities; over half of our academic staff work in departments that are in the top 10 per cent in the UK in their field and can thus be classed as world leading. The College is in the top seven UK universities for research earnings and has an overall annual income of nearly £450 million.
King's has a particularly distinguished reputation in the humanities, law, the sciences (including a wide range of health areas such as psychiatry, medicine, nursing and dentistry) and social sciences including international affairs. It has played a major role in many of the advances that have shaped modern life, such as the discovery of the structure of DNA and research that led to the development of radio, television, mobile phones and radar. It is the largest centre for the education of healthcare professionals in Europe; no university has more Medical Research Council Centres.
The College is in the midst of a five-year, £500 million fundraising campaign – World questions|King's answers – created to address some of the most pressing challenges facing humanity as quickly as feasible. The campaign's three priority areas are neuroscience and mental health, leadership and society, and cancer. More information about the campaign is available at www.kcl.ac.uk/kingsanswers.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.kcl.ac.ukAll latest news from the category: Agricultural and Forestry Science
Newest articles

Magnetic tornado is stirring up the haze at Jupiter’s poles
Unusual magnetically driven vortices may be generating Earth-size concentrations of hydrocarbon haze. While Jupiter’s Great Red Spot has been a constant feature of the planet for centuries, University of California,…

Cause of common cancer immunotherapy side effect s
New insights into how checkpoint inhibitors affect the immune system could improve cancer treatment. A multinational collaboration co-led by the Garvan Institute of Medical Research has uncovered a potential explanation…

New tool makes quick health, environmental monitoring possible
University of Wisconsin–Madison biochemists have developed a new, efficient method that may give first responders, environmental monitoring groups, or even you, the ability to quickly detect harmful and health-relevant substances…



