Symbiotic bacteria in root cells may be key to producing better crops
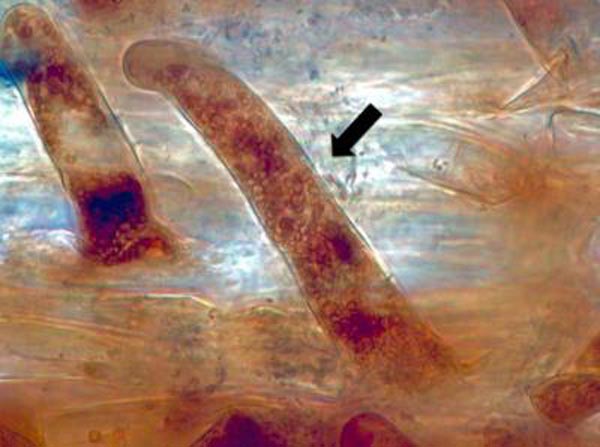
A Rutgers study finds that symbiotic bacteria that colonize root cells may be managed to produce hardier crops that need less fertilizer.
Credit: Rutgers University-New Brunswick
A Rutgers study finds that symbiotic bacteria that colonize root cells may be managed to produce hardier crops that need less fertilizer.
The study appears in the journal Microorganisms.
Bacteria stimulate root hair growth in all plants that form root hairs, so the researchers examined the chemical interactions between bacteria inside root cells and the root cell.
They found that bacteria are carried in seeds and absorbed from soils, then taken into root cells where the bacteria produce ethylene, a plant growth hormone that makes root cells grow root hairs. When the root hair grows, it ejects some of the bacteria back into the soil, then the remaining bacteria in the root hairs replicate and trigger a growth spurt every 15 minutes until the hairs are fully developed.
Ethylene is also a stress hormone that causes plants to adapt and become more resistant to oxidative stresses, including heat, soil salt, heavy metals and stresses potentially caused by climate change.
The researchers found that ethylene triggers root cells to secrete superoxide onto bacteria in root cells, causing bacteria to produce nitric oxide that detoxifies the superoxide. Nitric oxide combines with superoxide to form nitrate that is absorbed by root cells. In this process, bacteria in root cells make root hairs grow and supply root cells with nitrogen and other nutrients.
“This matters because it shows that the microbiome of plants is important for plant cell development, particularly root cell development, and nutrient supply,” said study co-author James White, a professor in the Department of Plant Biology in the School of Environmental and Biological Sciences at Rutgers University-New Brunswick. “Use of bacteria in plants may enable us to grow better developed and stress resistant crops that require less fertilizers, and thus will reduce environmental damage due to excess fertilizer applications with consequent runoff. Further, with the correct bacteria in crop plants, we may produce crops that are resistant to oxidative stresses stemming from climate perturbations, thus we may produce hardier and more resilient crops.”
###
Broadcast interviews: Rutgers University has broadcast-quality TV and radio studios available for remote live or taped interviews with Rutgers experts. For more information, contact John Cramer at john.cramer@rutgers.edu
ABOUT RUTGERS–NEW BRUNSWICK
Rutgers University-New Brunswick is where Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey, began more than 250 years ago. Ranked among the world’s top 60 universities, Rutgers’s flagship is a leading public research institution and a member of the prestigious Association of American Universities. It has an internationally acclaimed faculty, 12 degree-granting schools and the Big Ten Conference’s most diverse student body.
All latest news from the category: Agricultural and Forestry Science
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



