From Molecular Rendezvous to Brain Disease
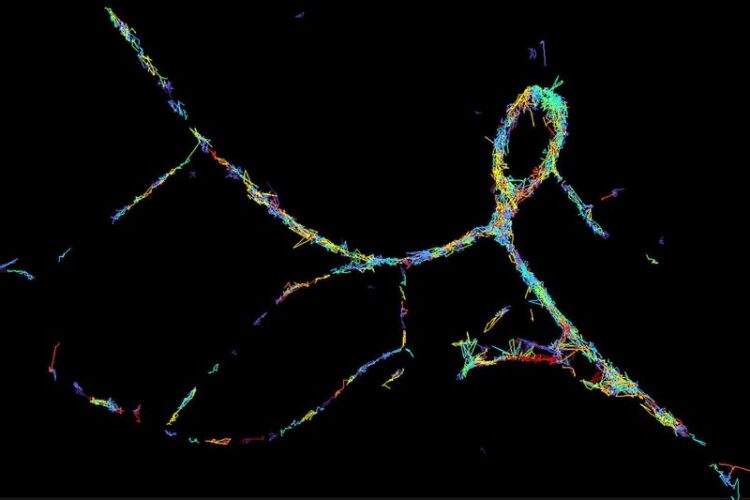
This microscopy image traces the movement of a single synaptic protein over a period of about 100 milliseconds. Source: DZNE / Milovanovic Lab
Previous
1.5 Million Euros for Berlin Researcher…
Dr. Dragomir Milovanovic, a neuroscientist at DZNE’s Berlin site, has been awarded an European Research Council (ERC) “Starting Grant” worth 1.5 million euros to investigate biophysical phenomena relevant to brain diseases in a groundbreaking research project. Ultimately, the goal is to better understand the behavior of aberrant protein inclusions in neurodegenerative diseases.
Human cells are complex entities comprising proteins, lipids and a wide number of other molecular spieces, some of them forming organized compartments, while others virtually float around. “The cell interior is by no means a homogeneous mass. It contains various constituents like the mitochondria, known as the powerhouses of the cell, or the nucleus that holds the genome,” says Milovanovic. “And there are other intricate structures that are essential for the cell’s proper functioning. All these so-called organelles are embedded in a fluid, the cytosol, which is a kind of cocktail of different ingredients.”
Microscopic droplets
Against this background, the Berlin scientist conceived the now funded research project “MemLessInterface”, with which he aims to elucidate how different constituents inside neurons interact. A question significant not only for regular operation, but also for pathological processes such as those that occur in neurodegeneration. Specifically, Milovanovic and his team will be studying the contact between membranes and so-called biomolecular condensates. “Some of the cell organelles are encased in a hull of fatty molecules, referred to as membrane. On the other hand, in the cytosol, we have biomolecular condensates that resemble tiny droplets suspended inside a larger liquid, and which have no such membranes,” he explains.
Close encounters
“Biomolecular condensate” is a generic term that describes fluid-like behavior rather than chemical composition. In fact, these condensates can comprise a wide variety of biopolymers: for example, assemblies of proteins, nuclein acids, or even more complex structures. Failure to regulate these condensates occurs in Alzheimer’s, Lewy Body dementia and other neurodegenerative disorders. As a consequence, abnormal proteins cluster together, contributing to cellular dysfunction and neuronal loss. However, biomolecular condensates also exist in healthy cells. “It is currently agreed that these condensates are involved in cellular functions like packaging of nucleic acids or for communication between neurons. To do so, they need to interact with other cell compartments, especially with organelles surrounded by membranes”, Milovanovic says. Yet, at present there is no understanding of what happens when organelles with membranes meet biomolecular condensates. “Do they stay together or do they separate again? And what does that depend on? This is where my project comes in. I would like to find out what is going on during these molecular rendezvous. I hypothesize that this first encounter is crucial and determines whether it develops into a harmonious or a pathological relationship,” he says. “I don’t mean that just as a metaphor, it is really about the roots of neurodegeneration.”
The outer rim
To get to the bottom of this, the Berlin researcher and his team will be applying cutting-edge scientific methods. As a paradigm, the focus will be on “synaptic vesicle condensates”. They are assemblies of small bubbles held together by proteins that act like a liquid glue. These condensates occur at the outer rim of neurons, in the so-called synapse, where neurons connect. “Synaptic vesicle condensates consist of a biomolecular condensate represented by the cross-linking proteins, and they also contain membranes. Namely, the membranes forming the bubbles. This setting provides the opportunity to study interactions between these different components,” Milovanovic explains. „This will give us insights into the contact between membrane-less and membrane-bound cellular components. That’s important for understanding the regular function of neurons and also crucial in the context of brain diseases associated with protein aggregation.”
About the Deutsches Zentrum für Neurodegenerative Erkrankungen, DZNE (German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases): DZNE is a research institute funded by the German federal and state governments, comprising ten sites across Germany. It is dedicated to diseases of the brain and nervous system, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and ALS, which are associated with dementia, movement disorders and other serious health impairments. To date, there are no cures for these diseases, which represent an enormous burden for countless affected individuals, their families, and the healthcare system. The aim of DZNE is to develop novel strategies for prevention, diagnosis, care, as well as treatment, and to transfer them into practice. To this end, DZNE cooperates with universities, university hospitals, research centers and other institutions in Germany and abroad. The institute is a member of the Helmholtz Association and belongs to the German Centers for Health Research. https://www.dzne.de/en
Weitere Informationen:
https://www.dzne.de/aktuelles/pressemitteilungen/presse/vom-molekularen-rendezvo… German version of this press release
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Awards Funding
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



