Babe Ruth and earthquake hazard maps
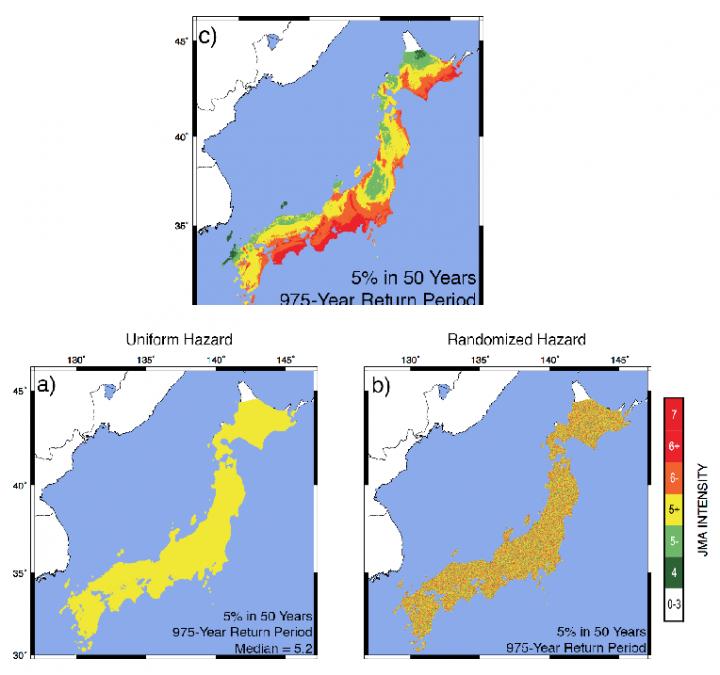
Here is a comparison of Japanese national earthquake hazard map (top) to uniform and randomized versions. The map predicts the level of shaking, shown by colors from red (highest) to white (least) expected to be exceeded at 5% of the sites on the map in the next 50 years. Surprisingly, by the most commonly used measure, the uniform and randomized maps work better than the published maps. Image courtesy of Seth Stein, Northwestern University.
Earthquake hazard maps use assumptions about where, when, and how big future earthquakes will be to predict the level of shaking. The results are used in designing earthquake-resistant buildings.
However, as the study's lead author, earth science and statistics graduate student Edward Brooks, explains “sometimes the maps do well, and sometimes they do poorly. In particular, the shaking and thus damage in some recent large earthquakes was much larger than expected.”
Part of the problem is that seismologists have not developed ways to describe how well these maps perform. As Seth Stein, William Deering Professor of Geological Sciences explains “we need the kind of information the weather service has, where they can tell you how much confidence to have in their forecasts.”
The question is how to measure performance. Bruce Spencer, professor of statistics, explains that “it's like asking how good a baseball player Babe Ruth was. The answer depends on how one measures performance. In many seasons Ruth led the league in both home runs and in the number of times he struck out. By one measure he did very well, and by another, very poorly. In the same way, we are using several measures to describe how hazard maps perform.”
Another problem is that the hazard maps try to forecast shaking over hundreds over years, because buildings have long lifetimes. As a result, it takes a long time to tell how well a map is working. To get around this, the team looked backwards in time, using records of earthquake shaking in Japan that go back 500 years.
They compared the shaking to the forecasts of the published hazard maps. They also compared the shaking to maps in which the expected shaking was the same everywhere in Japan, and maps in which the expected shaking at places was assigned at random from the published maps.
The results were surprising. In Brook's words “it turns out that by the most commonly used measure using the uniform and randomized maps work better than the published maps. By another measure, the published maps work better.”
The message, in Stein's view, is that seismologists need to know a lot more about how these maps work. “Some of the problem is likely to be that how earthquakes occur in space and time is more complicated that the maps assume. Until we get a better handle on this, people using earthquake hazard maps should recognize that they have large uncertainties. Brightly colored maps look good, but the earth doesn't have to obey them and sometimes won't.”
###
This research will be presented at the 2015 Annual Meeting of the Geological Society of America in Baltimore, MD, as part of the Bridging Two Continents joint “meeting-within-a meeting” with the Geological Society of China.
CONTACTS:
Edward Brooks, eddie@earth.northwestern.edu, 215-630-5436
Seth Stein, s-stein@northwestern.edu, 847-308-3806
WHAT:
Session 6
Active Intracontinental Tectonics in Asia and North America and the Associated Geohazards
session link: https:/
Paper 6-12, Using Historical Intensity Data To Assess Long-Term Performance of Earthquake Hazard Maps
Abstract link: https:/
WHERE & WHEN:
Sunday, 1 November 2015: 8:00 AM-12:00 PM
Room 349/350 (Baltimore Convention Center)
Presentation Time: 11:20 AM
The Geological Society of America, founded in 1888, serves more than 27,000 members from academia, government, and industry in more than 100 countries. Through its meetings, publications, and programs, GSA enhances the professional growth of its members and promotes the geosciences in the service of humankind. GSA encourages cooperative research among earth, life, planetary, and social scientists, fosters public dialogue on geoscience issues, and supports all levels of earth science education.
Figure caption: Comparison of Japanese national earthquake hazard map (top) to uniform and randomized versions. The map predicts the level of shaking, shown by colors from red (highest) to white (least) expected to be exceeded at 5% of the sites on the map in the next 50 years. Surprisingly, by the most commonly used measure, the uniform and randomized maps work better than the published maps. Image courtesy of Seth Stein, Northwestern University.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



