Global warming will leave different fingerprints on global subtropical anticyclones
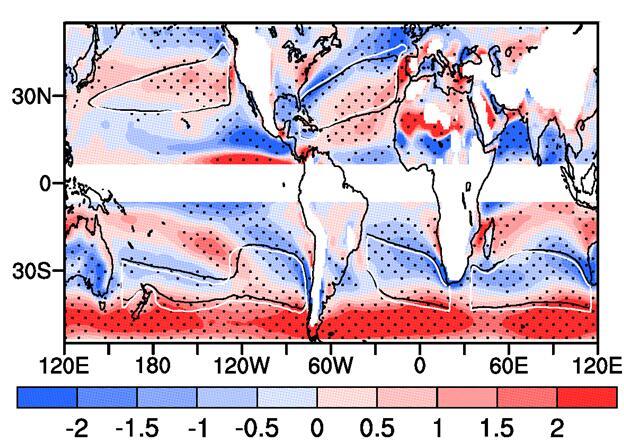
Projected future change of relative vorticity at 925 hPa. The black and white contours show the climatology for the 20th and 21st centuries. The shading shows the projected change by the ensemble mean of 30 models, and projected sign of change agreed by more than 70% of the models is stippled. Credit: He et al, 2017
To assess the possible responses of the subtropical anticyclones to greenhouse gases (GHG) forcing, Dr. HE Chao from China Meteorological Administration, and Drs. WU Bo, ZOU Liwei and Prof. ZHOU Tianjun from CAS Institute of Atmospheric Physics adopted multiple metrics and obtained robust results.
Coupled models under GHG forcing show that the subtropical anticyclones over North Pacific, South Atlantic and South Indian Ocean will become weaker in future under RCP8.5 scenario, whereas the subtropical anticyclones over North Atlantic and South Pacific will become stronger.
“Intensity change of the subtropical anticyclones to GHG forcing is dominated by two factors — the enhanced tropospheric static stability and the pattern of change in diabatic heating”, said Dr. HE. “The tropospheric static stability is enhanced via moist adiabatic adjustment under GHG forcing, and it acts to reduce the intensity of all the subtropical anticyclones. Meanwhile, the pattern of change in the tropospheric diabatic heating acts to weaken the North Pacific subtropical anticyclone but to enhance the subtropical anticyclones over North Atlantic and South Pacific.”
“Our findings show evidences that the global warming will have different impacts on the global subtropical anticyclones”, said Dr. ZOU Liwei, the co-author of the paper.
“The intensity of North Pacific subtropical anticyclone reduces significantly, since both the enhanced static stability and enhanced diabatic heating act to weaken it. Over South Atlantic and South Indian Ocean, the effect of enhanced static stability dominates, and the subtropical anticyclones over these two basins also become weaker. The effect of reduced diabatic heating overwhelms the effect of enhanced static stability over North Atlantic and South Pacific, and their combined effect enhances these two subtropical anticyclones.”
This study is recently published in Journal of Climate.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Pinpointing hydrogen isotopes in titanium hydride nanofilms
Although it is the smallest and lightest atom, hydrogen can have a big impact by infiltrating other materials and affecting their properties, such as superconductivity and metal-insulator-transitions. Now, researchers from…

A new way of entangling light and sound
For a wide variety of emerging quantum technologies, such as secure quantum communications and quantum computing, quantum entanglement is a prerequisite. Scientists at the Max-Planck-Institute for the Science of Light…

Telescope for NASA’s Roman Mission complete, delivered to Goddard
NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is one giant step closer to unlocking the mysteries of the universe. The mission has now received its final major delivery: the Optical Telescope…



