Meteorite impacts can create DNA building blocks
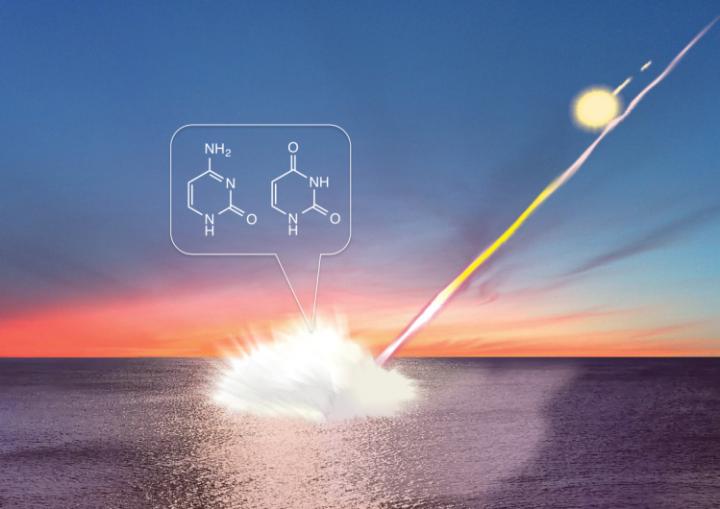
Figure 1: These are chematics of nucleobases formation by meteorite impact on earth. Credit Dr. Yoshihiro Furukawa
With precise analysis of the products recovered after impacts, the team found the formation of nucleobases and amino acids from inorganic compounds. The research is reported this week in the journal Earth and Planetary Science Letters.
All the genetic information of modern life is stored in DNA as sequences of nucleobases. However, formation of nucleobases from inorganic compounds available on prebiotic Earth had been considered to be difficult.
In 2009, this team reported the formation of the simplest amino acid, glycine, by simulating meteorite impacts. This time, they replaced the carbon source with bicarbonate and conducted hypervelocity impact experiments at 1 km/s using a single stage propellant gun (Figure 2).
They found the formation of a far larger variety of life's building blocks, including two kinds of nucleobases and nine kinds of proteinogenic amino acids. The results suggest a new route for how genetic molecules may have first formed on Earth.
###
Publication Details
Title: Nucleobases and amino acids formation through impacts of meteorites on the early ocean.
Authors: Furukawa Y., Nakazawa H., Sekine T., Kobayashi T., Kakegawa T.
Journal: Earth and Planetary Science Letters (2015), http://dx.
Contacts:
Dr. Yoshihiro Furukawa
Assistant Professor, Department of Earth Science, Tohoku University
Email: furukawa@m.tohoku.ac.jp
Tel: +81-22-795-3453
Dr. Takamichi Koybayashi
Principal Researcher, Ultra-High Pressure Processes Group
Materials Processing Unit, National Institute for Materials Science
Email: KOBAYASHI.Takamichi@nims.go.jp
Tel: +81-29-860-4419
Dr. Toshimori Sekine
Professor, Department of Earth and Planetary System Science, Hiroshima University
Email: toshimori-sekine@hiroshima-u.ac.jp
Tel: +81-82-424-7474
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



