Mystery of archaeal butane degradation solved
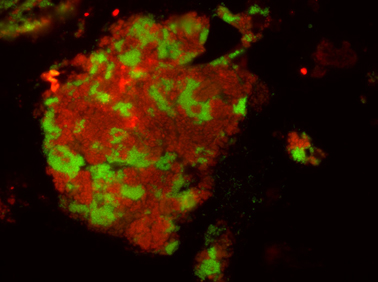
Cell specific visualization of the butane oxidizing consortia. In red the archaea Candidatus Syntrophoarcheum butanivorans, in green the bacteria Hotseep-1 Rafael Laso-Pérez. Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology and Victoria Orphan, Caltech, USA
Gaseous hydrocarbons in the seafloor
Natural gas is often released at the seafloor surface. In the upper sediment layers methane is formed by methanogenic archaea (see box). Economically more valuable gas reservoirs are however situated in deeper layers of the seafloor.
Here gas forms in purely chemical reactions from geothermally heated biomass of plant, animal and microbial origin. Along with methane, the thermogenic (thermally generated) gas contains other hydrocarbons such as propane and butane.
As anyone who has lit a gas stove, a lighter or started a gas powered car knows, burning gas requires oxygen. Also many microorganisms eat hydrocarbon gases by using oxygen, for instance in well-oxygenated top sediment layers. When the oxygen is used up, other microorganisms take over, however most of their metabolic solutions to activate and fully oxidize their substrate are completely unknown.
How microorganisms consume natural gas without molecular oxygen
Distinct microorganisms specialized on the anaerobic oxidation of different hydrocarbons. Even though methane is the simplest hydrocarbon, its anaerobic oxidation (AOM) coupled to sulfate reduction involves a team of two specific partners, archaeal and bacterial. The methane-oxidizing archaea (ANME) use similar enzymes as their methane-producing (methanogenic) relatives, however in reverse direction.
To activate the methane molecule these archaea produce large quantities of the enzyme Methyl-Coenzyme M Reductase (MCR). MCR binds the methane as methyl group to the sulfur compound coenzyme M, thereby starting the oxidation process which eventually leads to carbon dioxide (CO2).
The ANME however do not possess enzymes for sulfate reduction: this part of the AOM process is covered by the sulfate-reducing partner. On the other hand, the anaerobic oxidation of the larger gases, propane and butane, was found in bacteria that couple hydrocarbon oxidation to sulfate reduction in one cell.
The novel pathway for butane is based on the degradation of the anaerobic methane oxidation
In their latest research published in Nature microbiologists from Bremen, Leipzig, Göttingen and Bielefeld describes a new type of microbial consortia thriving on a butane diet. Similar to AOM these consortia also consist of archaeal and bacterial species. Surprisingly, the genomes of both partner organisms lack the typical genes for anaerobic butane activation.
“Instead we found genes distantly related to the MCR of methanogenic and methanotrophic archaea. Do the encoded enzymes have a role in butane oxidation?” thought PhD student Rafael Laso-Pérez, first author of the research article “And if that proves to be true, what other reactions would lead to a complete oxidation of butane to carbon dioxide?” Only painstaking lab work, and many different analyses, could solve this puzzle.
To validate this theory the microbiologist Dr. Florin Musat and his colleagues from the ProVIS at the UFZ in Leipzig used ultra-high resolution mass spectroscopy to look at intracellular metabolites. His team succeeded in identifying the forecasted intermediate – butyl-coenzyme M. “Up to date, methyl-coenzyme M reductases where known to be highly specific to the methane metabolism.
By proving the formation of butyl-coenzyme M in these archaea we demonstrate that this enzyme family can indeed handle larger hydrocarbons”, explains Dr. Musat. The research teams completed the pathway by finding other genes of the methanogenesis pathway and key elements of the butyrate and acetate metabolism.
“Combining these pathways in the right manner allows complete oxidation of butane in archaea. Evolution is ingenious: Some old tricks from other species were copied and adapted. This is known as horizontal gene transfer, this means that DNA sequences are taken from other species” explains Dr. Gunter Wegener, initiator of this study. “It was quite a long way to solve this puzzle and involved investigators from many different fields.”
Like their methane-consuming relatives the butane-oxidizing archaea are not able to fulfill the job on their own. As in AOM consortia the butane oxidizers have partner bacteria. “Electron microscopy shows tiny protein compounds connecting bacterial and archaeal cells. Electrons travel on these nanowires from the archaea to the bacteria that use them to reduce sulfate. We were able to show syntrophic electron exchange via protein nanowires for a second example,” says Dr. Gunter Wegener and adds:” Studying the archaea is like a journey in the past, and the coenzyme M reactions are among the earliest in the history of life”. All discovered species need a name – and so their new lab pet was baptized Candidatus Syntrophoarchaeum butanivorans – a butane-eating archaeon that needs a little help (syntrophy) by a partner for life.
Open questions remain
Where else on the planet do these archaea exist? Why and how did evolution lead to team work of microorganisms in consortia vs. microorganisms able to catalyze both oxidation and reduction reactions? Are there other variants of methyl-coenzyme M reductases able to activate even higher alkanes than butane? Such questions will keep researchers busy at the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology and the Helmholtz Zentrum für Umweltforschung (UFZ).
Please direct your questions to
Rafael Laso-Perez, Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology,
D-28359 Bremen, Phone: 0421 2028 867, rlperez@mpi-bremen.de
Dr. Gunter Wegener, Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology,
D-28359 Bremen, Phone: 0421 2028 867, gwegener@mpi-bremen.de
Dr. Florin Musat, Helmholtz-Zentrum für Umweltforschung (UFZ) Leipzig,
D-04318 Leipzig, Phone: 0341 235 1005, florin.musat@ufz.de
Or the press office
Dr. Manfred Schloesser and Dr. Fanni Aspetsberger
presse@mpi-bremen.de Phone: 0421 2028 704
Original publication
Thermophilic archaea activate butane via alkyl-CoM formation. Rafael Laso-Pérez, Gunter Wegener, Katrin Knittel, Friedrich Widdel, Katie J. Harding , Viola Krukenberg, Dimitri V. Meier, Michael Richter, Halina E. Tegetmeyer, Dietmar Riedel, Hans-Hermann Richnow, Lorenz Adrian, Thorsten Reemtsma, Oliver Lechtenfeld, Florin Musat. Nature, 2016 doi: 10.1038/nature20152
Participating Institutions
Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology, Bremen
MARUM, Zentrum für Marine Umweltwissenschaften, Universität Bremen
Max-Planck-Institut für Biophysikalische Chemie, Göttingen, Germany.
Alfred-Wegener-Institut, Helmholtz-Zentrum für Polar- und Meeresforschung, Bremerhaven
Centrum für Biotechnologie, Universität Bielefeld
Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research – UFZ, Leipzig
http://www.mpi-bremen.de Web site of the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



