NASA's Aqua Satellite Sees Hurricane Vance Headed for Landfall in Western Mexico
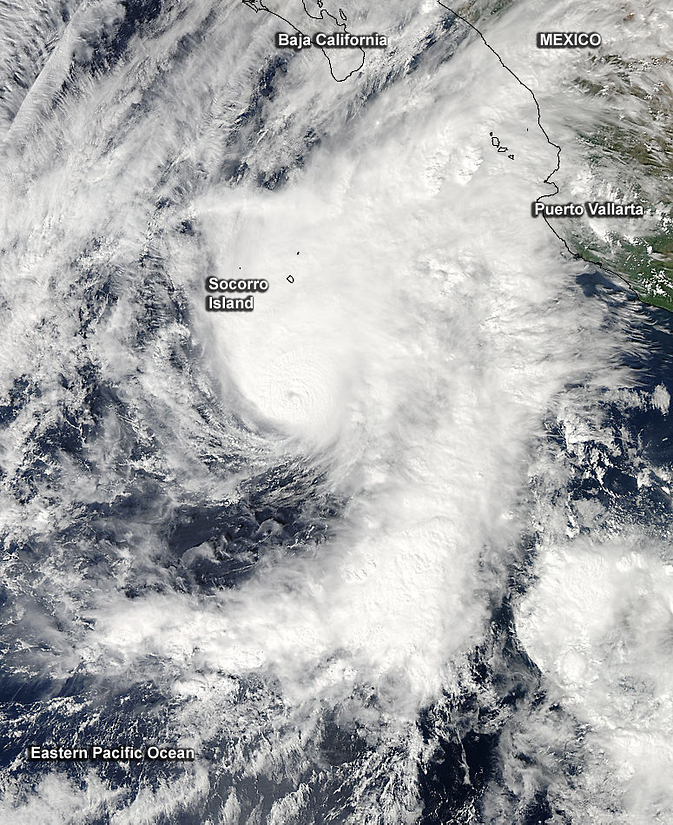
NASA's Aqua satellite saw Hurricane Vance off Mexico's west coast on Nov. 3. Clouds covered Socorro Island and stretched as far east as Puerto Vallarta. Image Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team
On Nov. 3 at 20:50 UTC (3:50 p.m. EST) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Hurricane Vance off Mexico's west coast.
The eastern quadrant of the storm covered Socorro Island and stretched as far east as Puerto Vallarta. Around the center of circulation were a thick band of strong thunderstorms that appeared bright white on the MODIS image. Vance's eye was no longer visible as it had filled in with clouds.
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) reported at 10 a.m. EST (7 a.m. PST/1500 UTC) on Nov. 4 that Vance's maximum sustained winds had decreased to 85 mph (140 kph) and rapid weakening was forecast.
The center of Hurricane Vance was located near latitude 19.3 north and longitude 109.6 west.
That puts the center of Vance about 100 miles (155 km) east-northeast of Socorro Island. Vance is moving toward the north-northeast near 13 mph (20 kph) and is expected to continue for the next couple of days.
Vance is expected to bring large amounts of rainfall to northwestern Mexico. Rainfall totals of 4 to
8 inches with isolated amounts near 12 inches through Wednesday, Nov. 5 over the states of Sinaloa, Nayarit and Durango in western Mexico. NHC noted that swells generated by Vance will be affecting portions of the coast of southwestern Mexico and Baja California Sur today and tonight.
Over the next 24 to 36 hours, Vance could weaken to a tropical depression by the time it reaches the coast of Mexico. Landfall is expected mid-day Wednesday, Nov. 5.
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/21e-eastern-pacific/All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



