NASA Satellite Imagery Shows Some Punch Left in System 94S
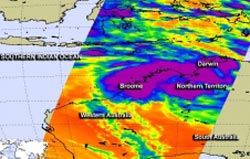
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over System 94S on January 15 at 11:59 a.m. EST and saw a band of powerful thunderstorms (purple) northwest of the center of the broad circulation center entering the Timor Sea from Northern Territory, Australia. <br>Image Credit: NASA JPL, Ed Olsen <br>
NASA's Aqua satellite showed that thunderstorms in the low had the potential for heavy rain as it continues to track over land, and heavy rainfall warnings are in effect in the Northern Territory.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over System 94S on January 15 at 11:59 a.m. EST and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument saw a band of powerful thunderstorms northwest of the center of the broad circulation center entering the Timor Sea from Northern Territory, Australia. Some of the thunderstorms were very high, and cloud top temperatures colder than -63F/-52C. Those temperatures are conducive to a NASA study that indicates the potential for those storms to have heavy rainfall rates.
On January 16 at 08:30 UTC/3:30 a.m. EST/6 p.m. Darwin local time, System 94S was centered about 370 nautical miles east of Broome, Australia near 18.6 south and 128.6 east. System 94S continues to track to the west and computer models indicate that it may re-emerge in the waters of the Southern Indian Ocean in the next 4 to 5 days.
The Australian Government Bureau of Meteorology or ABM for the Northern Territory issued a Severe Weather Warning for heavy rainfall and flash flooding on January 16 as the low continued to move slowly west. The warning was for residents in the Victoria River and northwest Alice Springs Districts and it was issued at 10:29 p.m. CST/local time.
At 1200 UTC/7 a.m. EST/9:30 p.m. CST/Darwin local time, System 94S was centered near latitude 19.5 south and longitude 128.7 east about 99.4 miles/160 kilometers west northwest of Rabbit Flat. The ABM forecasts the low to move south along the western border of the Northern Territory.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center or JTWC reported that animated multispectral satellite imagery and the radar loop from Halls Creek, Australia, showed a defined circulation center with several bands of convection wrapping around the center (which is still over land). Maximum sustained surface winds were estimated as high as 20 knots.
Currently, the JTWC gives this system a low chance for development into a tropical cyclone over the next day or two.
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



