New technique separates industrial noise from natural seismic signals
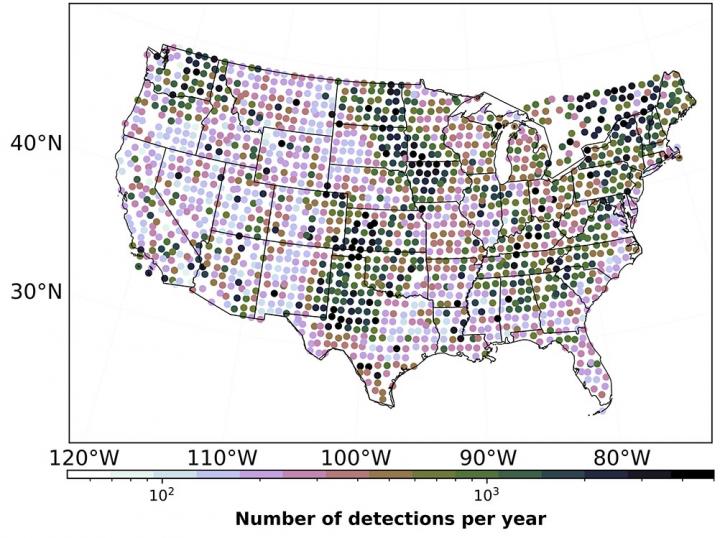
Map of detected industrial noise across the contiguous United States. Credit: Los Alamos National Laboratory
For the first time, seismologists can characterize signals as a result of some industrial human activity on a continent-wide scale using cloud computing.
In two recently published papers in Seismological Research Letters, scientists from Los Alamos National Laboratory demonstrate how previously characterized “noise” can now be viewed as a specific signal in a large geographical area thanks to an innovative approach to seismic data analyses.
“In the past, human-caused seismic signals as a result of industrial activities were viewed as 'noise' that polluted a dataset, resulting in otherwise useful data being dismissed,” said Omar Marcillo, a seismologist at Los Alamos National Laboratory and lead author of the study.
“For the first time, we were able to identify this noise from some large machines as a distinct signal and pull it from the dataset, allowing us to separate natural signals from anthropogenic ones.”
The study used a year's worth of data from more than 1,700 seismic stations in the contiguous United States. Marcillo detected approximately 1.5 million industrial noise sequences, which corresponds on average to around 2.4 detections per day at each station.
“This shows us just how ubiquitous industrial noise is,” said Marcillo. “It's important that we're able to characterize it and separate it from the other seismic signals so we can understand exactly what we're looking at when we analyze seismic activity.”
This data was accessed and processed using cloud computing–a novel approach that allows for greater scalability and flexibility in seismological research. The approach is detailed in a companion paper, which demonstrated how cloud computing services can be used to do large-scale seismic analysis ten times faster than traditional computing, which requires data to be downloaded, stored, and processed.
Using Amazon Web Services' cloud computing, researchers were able to acquire and process 5.6 terabytes of compressed seismic data in just 80 hours. To do this using traditional computing methods would have taken several weeks.
Marcillo said that his work to characterize industrial noise across the country would not have been possible without this new cloud-computing approach. “My colleagues and I had figured out how to separate the industrial noise signal from the rest of the seismic signal, but we couldn't scale it,” he said.
So Marcillo collaborated with Jonathan MacCarthy to find a way to expand it to cover a large geographical area; cloud computing was the answer. It is also flexible enough to adapt to the evolving needs of many research applications, including processing speed, memory requirements, and different processing architectures.
“Seismology is a data-rich field,” said MacCarthy, lead author of the paper on the cloud-based approach. “Previously, seismic data would have to be downloaded and processed by each individual researcher. Cloud computing allows all of that data to be stored in one place, and for researchers to easily access and work with it in a community-based way. It's a huge development and has the potential to totally transform the way seismological research on large datasets is done.”
###
Research papers
Omar E. Marcillo, Jonathan MacCarthy; Mapping Seismic Tonal Noise in the Contiguous United States. Seismological Research Letters ; 91 (3): 1707-1716. doi: https:/
Jonathan MacCarthy, Omar Marcillo, Chad Trabant; Seismology in the Cloud: A New Streaming Workflow. Seismological Research Letters ; 91 (3): 1804-1812. doi: https:/
About Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory, a multidisciplinary research institution engaged in strategic science on behalf of national security, is managed by Triad, a public service oriented, national security science organization equally owned by its three founding members: Battelle Memorial Institute (Battelle), the Texas A&M University System (TAMUS), and the Regents of the University of California (UC) for the Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
Los Alamos enhances national security by ensuring the safety and reliability of the U.S. nuclear stockpile, developing technologies to reduce threats from weapons of mass destruction, and solving problems related to energy, environment, infrastructure, health, and global security concerns.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1785/0220190355All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



