Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
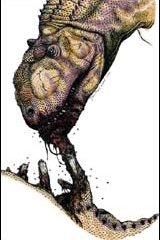
The exotic island of Madagascar, situated off the southeast coast of Africa, was a dangerous place to live 65 million to 70 million years ago. Crocodiles swarmed in the rivers, and a 30-foot-long, meat-eating dinosaur named Majungatholus atopus stalked the plains. Like most carnivorous dinosaurs, Majungatholus had teeth perfectly suited for ripping into flesh. But what was on the menu? Until now, this question has remained a mystery. In a report published in the April 3 issue of the Journal

Scientists using NASA satellite data have found the most intense global pollution from fires occurred during droughts caused by El Niño. The most intense fires took place in 1997-1998 in association with the strongest El Niño event of the 20th century.
Bryan Duncan, Randall Martin, Amanda Staudt, Rosemarie Yevich and Jennifer Logan, from Harvard University, used data observed by NASA’s Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) satellite to quantify the amount of smoke pollution from biomass b

Just as vegetables are essential to balancing the human diet, the inclusion of vegetation may be equally essential to balancing Earth’s climate models.
Scientists at MIT who were trying to create accurate models of climate change in the southern portion of the Sahara desert found that including a realistic component of vegetation growth and decay was absolutely essential. Without including the vegetation as a variable (rather than a fixed parameter), the models were not able to show the regi

A 161 million-year-old Mongolian fossil not only reveals a new species of salamanders, but also provides proof that much of the evolution of salamanders occurred in Asia.
For more than three years, scientists from the University of Chicago and Peking University in Beijing have been collecting thousands of salamander fossils, many of which preserve the entire skeleton and impressions of soft tissues, from seven excavation sites in Mongolia and China. Prior to the discovery in 1996 of the Chin

Researchers at Harper Adams University College, Shropshire, believe a ‘memory’ in the climate system could be tapped to improve long-range weather forecasts.
In the April edition of ‘Weather,’ the journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, an article co-written by Dr Peter Kettlewell will show how summer rainfall levels in the UK are affected by ‘remembered’ changes in winter air pressure over the North Atlantic ocean. The article is based upon the work of a team headed by Dr Kettlewell,

David L. Rodland, a Ph.D. student in Virginia Tech’s Department of Geological Sciences, has been studying encrustation, or the colonization of seashells by other marine organisms that live permanently attached to hard surfaces.
Examples of encrusting organisms (or epibionts) include serpulid and spirorbid worms, bryozoans, barnacles, and algae. Many epibionts produce their own calcareous tubes, shells, or skeletons, which are attached to that surface and may become fossilized along wit