Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.

The melting of an Antarctic ice sheet roughly 14,000 years ago triggered a period of warming in Europe that marked the beginning of the end of the Earth’s last ice age, says a new study.
A paper in the March 14 issue of the journal Science suggests that a catastrophic collapse of an Antarctic ice sheet dumped roughly a million cubic litres per second of freshwater into the southern oceans, changing the climate thousands of kilometres to the north and ushering in a dramatic climate shift kn
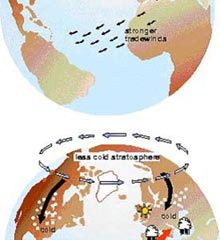
A recent NASA-funded study has linked the 1991 eruption of the Mount Pinatubo to a strengthening of a climate pattern called the Arctic Oscillation. For two years following the volcanic eruption, the Arctic Oscillation caused winter warming over land areas in the high and middle latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere, despite a cooling effect from volcanic particles that blocked sunlight.
One mission of NASA’s Earth Science Enterprise, which funded this research, is to better understand how th

When were the mountains of Wales pushed up?
It was well before the dinosaurs roamed the earth. And it happened in the aftermath of a gigantic continental collision, when England and Wales (then attached to southern Newfoundland) crashed into Scotland (then attached to north America). The muds of the sea floor were converted, then, into the hard grey slates of the Welsh hills.
Until now it has been very hard to tell exactly when these slates were formed, because the miner

Thanks to recent advances in parallel computing, an interdisciplinary team of scientists at the University of California, Santa Barbara has discovered a peculiar and important aspect of how seismic waves are generated during an earthquake. The results are published in the March 7 edition of Science Magazine.
The team, whose work is supported by the Keck Foundation, was composed of physics graduate student Eric M. Dunham, professor of physics Jean M. Carlson, and postdoctoral researcher Pasca

For centuries, they wouldn’t be caught dead next to each other.
But now a team of geologists directed by Joshua Smith, Ph.D., assistant professor of earth and planetary sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, have found a well-preserved fossil of a crab within inches of a tail vertebra from a massive plant-eating dinosaur.
This well-preserved fossil of a crab was found within inches of a dinosaur tail in Egypt’s Bahariya Oasis, the first evidence in literature of t

New findings from Queen’s researchers will help experts better predict future drought patterns and water availability in the prairies.
An international research team including biologists Kathleen Laird and Brian Cumming from the Queen’s Paleoecological Environmental Assessment and Research Laboratory (PEARL), and Peter Leavitt from the University of Regina, investigated records of drought over the past 2000 years from lake sediments in the northern Canadian prairie region (Manitoba