Study offers new insights on hurricane intensity, pollution transport
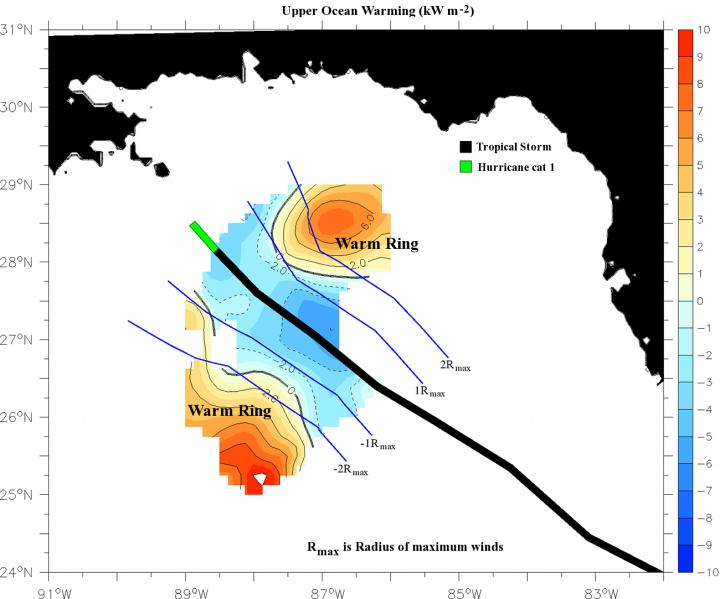
The figure depicts the upper ocean warming (in red color) observed over the warm rings during the intensification of Isaac. Credit: Benjamin Jaimes
As tropical storm Isaac was gaining momentum toward the Mississippi River in August 2012, University of Miami (UM) researchers were dropping instruments from the sky above to study the ocean conditions beneath the storm. The newly published study showed how a downwelling of warm waters deepened the storm's fuel tank for a rapid intensification toward hurricane status. The results also revealed how hurricane-generated currents and ocean eddies can transport oil and other pollutants to coastal regions.
Tropical storms obtain their energy from the ocean waters below. As a storm moves across the Gulf of Mexico, it may interact with an upwelling of cooler waters from the deeper ocean or, in the case of Isaac, a downwelling inside rings of warm water that separated from a warm-water current, called the Loop Current, that moves through the Gulf of Mexico to join with the Gulf Stream along the U.S. East Coast. As the storm moves forward, ocean temperatures are fueling the storm's intensity.
UM Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science researchers, in collaboration with NOAA's Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, deployed a total of 376 airborne sensors during six NOAA hurricane hunter aircraft flights conducted before, during, and after the passage of Isaac over the eastern Gulf of Mexico. The researchers observed a predominant downwelling of water inside these warm-water rings, or eddies, from the Loop Current, which caused its intensification from a tropical storm to a category 1 hurricane just prior to landfall.
“These results underscore the need for forecast models to include upwelling-downwelling responses to improve intensity forecasting and current transport,” said Benjamin Jaimes, an assistant scientist at the UM Rosenstiel School.
“Isaac moved over the region of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill where we observed both upwelling and downwelling processes that can re-suspend hydrocarbons lying on the seafloor,” said Nick Shay, professor of ocean sciences at the UM Rosenstiel School. “This may have resulted in tar balls being deposited on beaches by hurricane-generated currents.”
Tropical storm Isaac gradually intensified in the Gulf of Mexico to reach category 1 hurricane status as an 80 mph (130 km/h) storm, making landfall along the coast of Louisiana. The storm was estimated to have caused $2.39 billion in damage along its track.
###
The study, titled “Enhanced Wind-Driven Downwelling Flow in Warm Oceanic Eddy Features during the Intensification of Tropical Cyclone Isaac (2012): Observations and Theory,” was published in the June 2015 issue of the Journal of Physical Oceanography. The study's co-authors include: Benjamin Jaimes and Lynn “Nick” Shay of the UM Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science's Department of Ocean Sciences. BP/Gulf of Mexico Research Initiative to the Deep-C consortium at Florida State University supported the research.
About the University of Miami's Rosenstiel School
The University of Miami is one of the largest private research institutions in the southeastern United States. The University's mission is to provide quality education, attract and retain outstanding students, support the faculty and their research, and build an endowment for University initiatives. Founded in the 1940's, the Rosenstiel School of Marine & Atmospheric Science has grown into one of the world's premier marine and atmospheric research institutions. Offering dynamic interdisciplinary academics, the Rosenstiel School is dedicated to helping communities to better understand the planet, participating in the establishment of environmental policies, and aiding in the improvement of society and quality of life. For more information, visit: http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



