Suomi NPP satellite sees Molave on the move
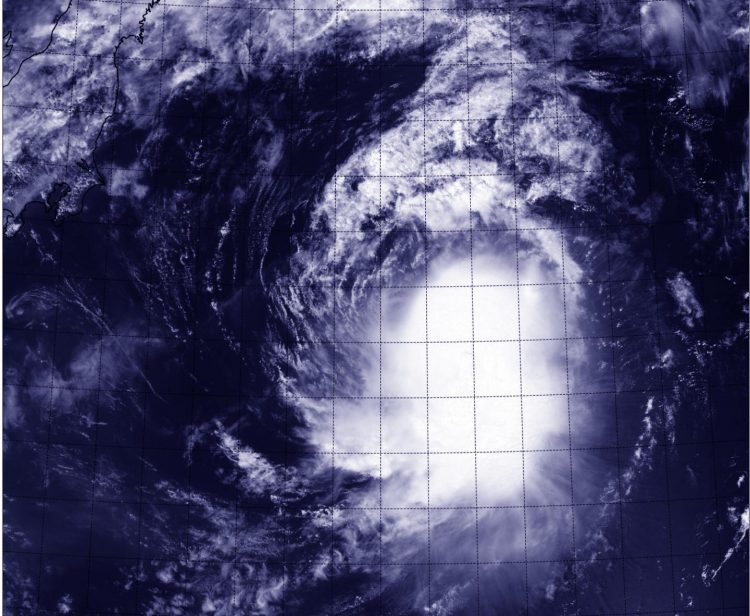
The VIIRS instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi satellite captured this visible picture of Tropical Storm Molave on Aug. 12 at 02:53 UTC. Credits: UW-CIMSS/NASA/NOAA
The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite or VIIRS instrument aboard the satellite provided a visible image of the storm that showed the bulk of showers were southeast of the center of circulation.
The clouds and thunderstorms were being pushed southeast by northwesterly wind shear between 10 and 20 knots/11.5 to 23.0 mph/18.5 to 37.0 kph. The Advanced Scatterometer (ASCAT) wind data showed that the strongest winds were in that same southeastern quadrant.
VIIRS is a scanning radiometer that collects visible and infrared imagery and “radiometric” measurements. Basically it means that VIIRS data is used to measure cloud and aerosol properties, ocean color, sea and land surface temperature, ice motion and temperature, fires, and Earth's albedo (reflected light).
On August 12, 2015 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT) Tropical Storm Molave had maximum sustained winds near 40 knots (46 mph/74 kph). It was centered near 33.8 North latitude and 149.9 East longitude, about 512 nautical miles east of Yokosuka, Japan. Molave was moving to the east at 13 knots (15 mph / 24 kph) and away from Japan.
Molave is moving east-northeast and forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect it to intensify a little to 50 knots because it will be tracking through sea surface temperatures near 26.6 Celsius (80 Fahrenheit). Molave is then expected to become extra-tropical south of Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Scientists transform blood into regenerative materials
… paving the way for personalized, blood-based, 3D-printed implants. Scientists have created a new ‘biocooperative’ material based on blood, which has shown to successfully repair bones, paving the way for…

A new experimental infection model in flies
…offers a fast and cost-effective way to test drugs. Researchers at the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute and Hospital have reinforced their leading role in infectious disease research by…

Material developed with novel stretching properties
KIT researchers produce metamaterial with different extension and compression properties than conventional materials. With this material, the working group headed by Professor Martin Wegener at KIT’s Institute of Applied Physics…



