Uranium chemistry and geological disposal of radioactive waste
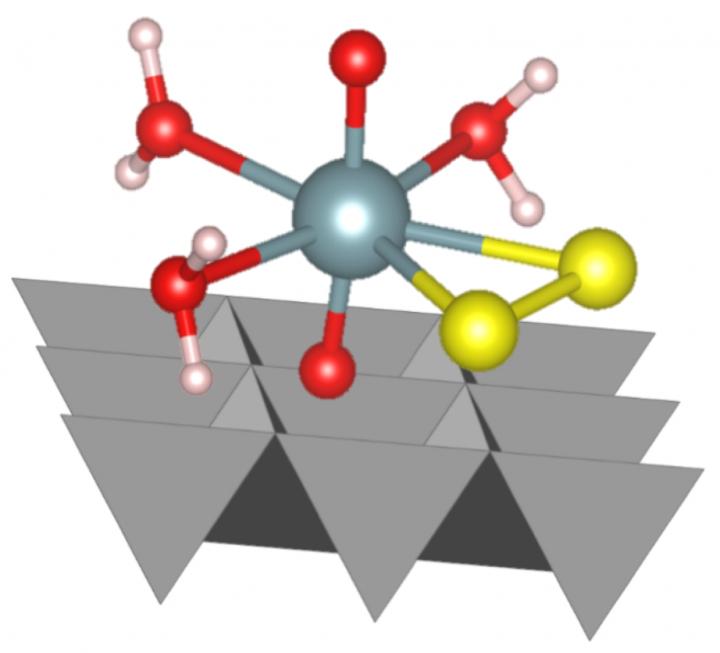
The uranium-persulfide complex associated with the transforming mineral surface. Credit: Diamond Light Source
A new paper to be published on 16 December provides a significant new insight into our understanding of uranium biogeochemistry and could help with the UK's nuclear legacy.
Conducted by a team of researchers from the University of Manchester, Diamond Light Source and Radioactive Waste Management, their work shows for the first time how uranium forms a uranium-sulfur complex under conditions generally found in the environment and how this compound can be an important intermediary in uranium immobilisation.
Published in Environmental Science & Technology, the paper is called “Formation of a U(VI)-persulfide complex during environmentally relevant sulfidation of iron (oxyhydr)oxides” 1
Professor Katherine Morris, Associate Dean for Research Facilities in the Faculty of Science and Engineering, University of Manchester and the Research Director for the BNFL Research Centre in Radwaste Disposal explains why recreating and studying these chemical complexes is highly relevant for understanding and dealing with radioactive waste.
She explains: “To be able to predict the behaviour of the uranium during geological disposal, we need to take into account that it may have interacted with other processes taking place in the ground. These so-called biogeochemical reactions are often a complex set of interactions between dissolved chemical species, mineral surfaces, and microorganisms.”
The recent study is the first time that researchers have shown that a uranium-sulfide complex can form under conditions representative of a deep underground environment. This complex then transforms further into highly immobile uranium oxide nanoparticles.
In the experiment, the researchers studied uranium when it sits at the surface of the mineral ferrihydrite, which is a widespread mineral in the environment. The researchers used an X-ray based method called X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS) to study the samples at Diamond Light Source, the UK's national Synchrotron. The XAS data, in combination with computational modelling, showed that during the sulfidation reaction, a short-lived and novel U(VI)-persulfide complex formed during this biogeochemical process.
Professor Sam Shaw, Co-Investigator and Professor of Environmental Mineralogy at the University of Manchester; “Shining the synchrotron beam onto the sample causes the uranium within to emit X-rays. By analysing the X-ray signal from the samples our team were able to determine the chemical form of uranium, and to which other elements it is bound.
To further validate the theory on the formation pathway of the uranium-sulfur complexes, our team also made computer simulations to conclude which type of complex is more likely to form. This is the first observation of this form of uranium under aqueous conditions, and provides new insight into how uranium behaves in environments where sulfide is present. This work
demonstrates the deep understanding we can develop of these complex systems and this knowledge will help underpin efforts to manage radioactive wastes in a geological disposal facility.”
Dr Luke Townsend, Postdoctoral Fellow in Environmental Radiochemistry at The University of Manchester, who undertook this research as part of his PhD further adds:
“When trying to mimic environmental processes in the laboratory, it's a challenge to produce accurate, high quality, reproducible science with such complex experiments, whilst also maintaining relevance to the geodisposal environment. However, obtaining exciting results such as these makes all the hard work and commitment to the project from myself and the group, both in our labs in Manchester and on the beamlines at Diamond, completely worthwhile.”
The XAS measurements were performed at Diamond on beamlines I20 and B18 by the researchers who used highly controlled sulfidation experiments that mimic biogeochemical processes in the deep underground environment. This was combined with geochemical analyses and computational modelling to track and understand uranium behaviour.
Physical Science Director at Diamond, Laurent Chapon concludes; “This is another example of how Diamond's state of the art analytical tools are enabling scientists to follow complex processes and help them to tackle 21st century challenges. In this instance, our beamlines allowed the users to gain real insight into the environmental relevance of this new uranium-sulfur complex, which feeds into our understanding of geological disposal.”
###
1 http://dx.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b03180All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



