
Dynamic Stop Pooling: Enhancing Sustainability in Shared Rides
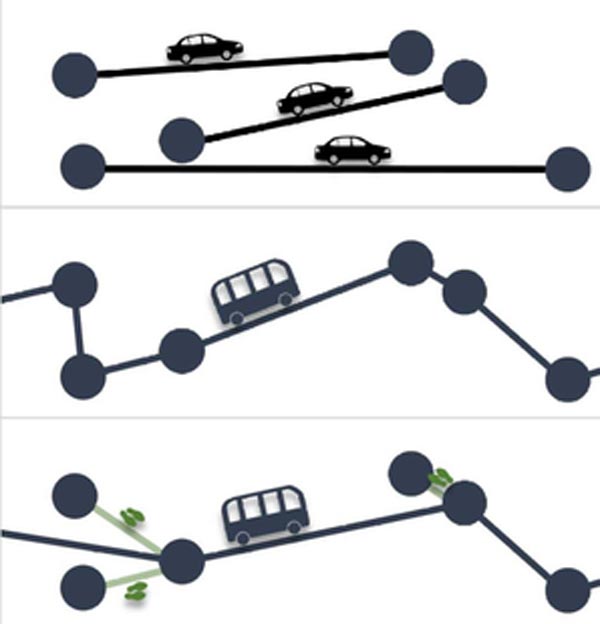
Ride sharing busses (middle) combine direct trips of multiple users and drive shorter in total than the sum of the individual car routes (top). When users walk to a nearby stop, buses drive even shorter routes while maintaining the user travel times (bottom).
(c) Charlotte Lotze
Introducing dynamic stop pooling.
Sustainable mobility is an important research field of the Chair of Network Dynamics (headed by Prof. Marc Timme) at the Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden (cfaed) at TU Dresden. Here, the chair’s researchers put a strong focus on “ride sharing”, i.e. the bundling of simultaneous trips of several people in one vehicle. A recently published study on this topic addresses the question how a dynamic combination of nearby stops enables more efficient ride sharing services.
The transportation sector causes about one-fifth of all climate-damaging emissions in Germany. One promising approach to reduce the carbon footprint of the transport system is “shared mobility,” i.e. sharing trips with similar routes as in a flexibilized and widely available shared cab (ride sharing). Such a service requires fewer vehicles and reduces emissions. However, the complex collective dynamics pose a challenge when predicting the efficiency and sustainability of ride-sharing systems. Standard door-to-door ride sharing services trade reduced route length for increased user travel times and come with the burden of many stops and detours to pick up individual users. In general, the distance traveled per user decreases when more users share a bus, and the service becomes more sustainable. However, more users per bus yield more detours for each individual user. Ride sharing services trade increased sustainability for longer travel times.
In the new study, four scientists at the Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden (cfaed) at TU Dresden propose combining suitable nearby stops dynamically (dynamic stop pooling). Instead of serving all users exactly from their desired origin to their destination, users might walk a short distance to a nearby stop. In this way, one bus can collect multiple passengers at the very same stop. “Buses take more direct routes and stop less often. The special feature is that the stops are combined dynamically according to the current requests such that the bus routes remain flexible,” explains Charlotte Lotze, the study’s lead author.
The study shows that users wait and drive shorter if they only walk a short part of their trip. In this way, they travel faster on average with pooled stops than in a standard ride sharing service, despite the additional walking time. “As a result, fewer vehicles can serve the same users while maintaining the travel time if passengers are willing to walk a short distance to the pickup or from the drop-off to their destination,” Lotze says. “Dynamic stop pooling therefore enables a more efficient and more sustainable service with fewer vehicles without requiring users to plan for longer travel times,” adds Prof. Marc Timme, Head of the Chair of Network Dynamics.
The study has been published in the open-access journal “New Journal of Physics”. An abstract video of the study is available here: (YouTube, running time 3:13 min):
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Jd0uNIbmX8k
Title: Dynamic stop pooling for flexible and sustainable ride sharing
Authors: Charlotte Lotze, Philip Marszal, Malte Schröder, Marc Timme
New Journal of Physics, DOI: 10.1088/1367-2630/ac47c9
Link (open access article): https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/ac47c9
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
TU Dresden, Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden
Prof. Marc Timme, Chair of Network Dynamics
Phone: +49 351 463 43972
E-mail: marc.timme@tu-dresden.de
Matthias Hahndorf
Science Communications
Phone: +49 351 463 42847
E-mail: matthias.hahndorf@tu-dresden.de
Weitere Informationen:
Link (open access article): https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/ac47c9












