Many people will soon load up Easter baskets with chocolate candy for children and adults to enjoy. On its own, dark chocolate has health benefits, such as antioxidants that neutralize damaging free radicals. And a report in ACS Food Science & Technology suggests that packing the sweet treat with pre- and probiotics could make it more healthful. Flavoring agents, however, can affect many properties, including moisture level and protein content of the chocolate product. Probiotics, found in fermented foods such…

Desire drives remote-controlled rodents.
Remote-controlled rats could soon be detecting earthquake survivors or leading bomb-disposal teams to buried land mines.
Signals from a laptop up to 500 metres away make the rats run, climb, jump and even cross brightly lit open spaces, contrary to their instincts. The rodents carry a backpack containing a radio receiver and a power source that transmits the signals into their brains through electrical probes the breadth of a hair.

An article in the May issue of Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine suggests that much of the medical inspiration for Mary Shelley’s legendary novel Frankenstein came not from central Europe, but from a retired Scots physician living in Windsor. Christopher Goulding, a postgraduate student at the University of Newcastle upon Tyne, bases his claims on his PhD research into the scientific interests of the novelist’s husband, the poet Percy Shelley.
Most criticism of Mary Shelley’s much-in

Fatty diets or high alcohol intake during pregnancy may lead to diabetes in children
Women who consume a high fat diet or who drink significant amounts of alcohol during pregnancy may increase the risk of their child developing diabetes as an adult according to a study in the current edition of the Journal of Endocrinology.
A team led by Dr Sam Pennington of the Department of Biochemistry, Brody School of Medicine at East Carolina University has found that insulin resistance,

Is it possible to make components out of organic polymers (plastics) whose structure is such that severed nerves can grow right into them and connect with electrodes in a prosthetic hand, for example? This is one of the research fields for Tobias Nyberg at the Section for Biomolecular and Organic Electronics at Linköping University, Sweden.
Part of Tobias Nyberg’s dissertation is based on collaboration with cell biologist Helena Jerregård. Her task is to find ways to get tangled nerves to s

The flow of soap solutions through fibres is of great importance for the final result of the washing process. This is one of the conclusions from the research project of Annemoon Timmerman. She will defend her thesis on Monday 22 April at TU Delft. With this conclusion she supports a theory that was disbelieved for years by experts in the field. Timmerman: “I have now experimentally proven why the laundry is actually clean after less than half an hour of washing. Up to now, that was a mystery.” The r
A team of researchers from the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, in coordination with the Instituto Nacional de Técnica Aerospacial Esteban Terradas (INTA – Esteban Terradas National Institute of Aerospace Technology), is preparing for a person to jump from an altitude of 38,000 metres, on the edge of the stratosphere. This will be the highest altitude from which anybody has ever jumped, allowing for the first ever studies of human behaviour in such an extreme situation.
Parachutist Miguel

A research group of the Microtechnology Centre at Chalmers, MC2, at Chalmers University of Technology in Göteborg, Sweden, has developed an ultra-sensitive device for detecting the presence of organic molecules present in space. Organic material as far away from us as many thousands of light years can be discovered this way. The sensor, which has a world record for sensing low amounts of heat, will be a vital part in satellite systems for the Herschel Mission, a remote sensing satellite project at th

A project to develop effective techniques for the ‘surface pasteurisation’ of food led by the University of Bristol is being helped by a new technique developed by scientists at the University of the West of England. Officially titled ‘BUGDEATH’ the project, which in total has eight partners, is aimed at ‘Predicting microbial death during heat treatments on foods’.
Researchers based at the University of Bristol Food Refrigeration and Process Engineering Centre, have been looking at ‘steam p

By using the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) as a `time machine`, astronomers from the Universities of Edinburgh and Oxford in the UK and the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore in the USA have been able to trace back the history of massive elliptical galaxies. They have found that galaxies of this kind, which still exist today, were already luminous families of stars about 10 billion years ago when the universe was only one third its present age. Their latest observations suggest tha

Archaeologists of the University of Bonn have just begun the first of three series of excavation programmes in Xkipché on the Mexican peninsula of Yucatán. They are investigating the living conditions of the population shortly before the city was finally abandoned towards the end of the 10th century as well as the city?s role as the residence of local princes during the turbulent period of its decline.
The location of the find is in the vicinity of the world famous ruined city of Uxmal (rece

It is well known that tobacco consumption causes a respiratory disease called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), characterized by formation of emphysema and progressive destruction of the lung. When pulmonary vessels are altered in this disease, life expectancy of the patients worsens. It has not been possible to establish the cause, but it has been attributed to low oxygen concentration in the blood. However, changes in the pulmonary vessels have also been found in COPD

A new public opinion poll from MORI shows that over 60% of British adults expect the impossible from science.
The MORI poll, commissioned to mark the opening of the new Science Media Centre, shows that 71% of the public look to scientists to give an ‘agreed view’ about science issues and 61% expect science to provide 100% guarantees about the safety of medicines. Yet most scientists insist that science cannot and should not deliver either.
Dr Mark Peplow, Science Information Officer

Friction pushes a spinning egg from horizontal to vertical.
Mathematicians have cracked the conundrum of the spinning egg. A hard-boiled egg spun on its side flips upright because of friction between the egg and the table, they calculate 1 .
The egg’s elevation appears paradoxical. Its centre of gravity moves up – making the system seem to be gaining energy.
In fact, spinning energy, translated into a horizontal force, pushes the egg upright, sa

Footprints and a fire found from 20,000 years ago.
Handprints and footprints 20,000 years old reveal that people lived on the Tibetan plateau at the height of the Ice Age – 16,000 years earlier than scientists had thought. The newly found signs of life cast doubt on the idea that a glacier a kilometre thick covered the plateau at that time.
David Zhang and S. H. Li of the University of Hong Kong found the marks of at least six individuals, including two children, in marble-l
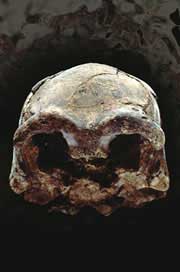
Ethiopian fossil suggests early humans were one big family.
A one-million-year-old skull unearthed in Ethiopia hints that our long-extinct cousins Homo erectus were a varied and widespread bunch, much like today’s humans. The find may undermine previous claims that H. erectus was in fact made up of two different species. Homo erectus , which means ’upright man’, appeared about 1.8 million years ago. Because of its posture and large brain, it is regarded as t

A new study shows that schools and many education programmes are failing to provide students with a basic understanding of evolution.
It is famously difficult to explain evolutionary principles without resorting to anthropomorphic or figurative language. Evolution ‘selects’ the fittest individuals; species ‘adapt’ to change. Both of these phrases are commonplace when explaining the very complex processes involved in evolution. However, this use of language implies that there is an agency o