A healthy lifestyle adds years to life
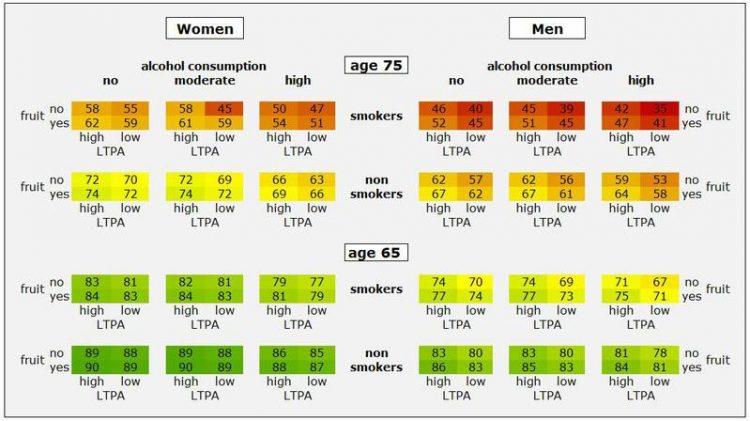
E.g.: a 75-year-old man today who at the start of the study smoked, drank a lot and hardly ate any fruit has a 35 percent probability of surviving the next ten years. UZH
This is the conclusion of a study by public health physicians at the University of Zurich who documented for the first time the impact of behavioural factors on life expectancy in numbers. The results are to be taken over into prevention and health counselling in primary care.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), cancer, diabetes and chronic respiratory disorders – the incidence of these non-communicable diseases (NCDs) is constantly rising in industrialised countries. The Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) is, therefore, in the process of developing a national prevention strategy with a view to improving the population’s health competence and encouraging healthier behaviour.
Attention is focusing, amongst other things, on the main risk factors for these diseases which are linked to personal behaviour – i.e. tobacco smoking, an unhealthy diet, physical inactivity and harmful alcohol consumption.
Against this backdrop Private Docent Brian Martin and his colleagues from the Institute of Social and Preventive Medicine (ISPM) at the University of Zurich have examined the effects of these four factors – both individual and combined – on life expectancy.
For the first time the consequences of an unhealthy lifestyle can be depicted in numbers. An individual who smokes, drinks a lot, is physically inactive and has an unhealthy diet has 2.5 fold higher mortality risk in epidemiological terms than an individual who looks after his health. Or to put it positively: “A healthy lifestyle can help you stay ten years’ younger”, comments the lead author Eva Martin-Diener.
Analysis of data from the Swiss Cohort
For the study the researchers used data from the Swiss National Cohort (SNC). The Zurich public health physicians focussed on CVDs and cancer as they account for the most deaths in Switzerland. The researchers succeeded in correlating data on tobacco consumption, fruit consumption, physical activity and alcohol consumption from 16,721 participants aged between 16 and 90 from 1977 to 1993 with the corresponding deaths up to 2008. The impact of the four forms of behaviour was still visible when biological risk factors like weight and blood pressure were taken into account as well.
“The effect of each individual factor on life expectancy is relatively high”, states Eva Martin-Diener. But smoking seems to be the most harmful. Compared with a group of non-smokers, smokers have a 57 percent higher risk of dying prematurely. The impact of an unhealthy diet, not enough sport and alcohol abuse results in an elevated mortality risk of around 15 percent for each factor. “We were very surprised by the 2.5 fold higher risk when all four risk factors are combined”, explains Brian Martin. Hence, the probability of a 75-year-old man with all risk factors surviving the next ten years is, for instance, 35 percent, without risk factors 67 percent – for a woman 47 and 74 percent respectively.
Effects only appear in later life
According to Martin an unhealthy lifestyle has above all a long-lasting impact. Whereas high wine consumption, cigarettes, an unhealthy diet and physical inactivity scarcely had any effect on mortality amongst the 45 to 55-year-olds, it does have a visible effect on 65 to 75-year-olds. The probability of a 75-year-old man with none of the four risk factors surviving the next ten years is 67 percent, exactly the same as the risk for a smoker who is ten years younger, doesn’t exercise, eats unhealthily and drinks a lot.
The social and public health physicians depict the dependency of life expectancy and the four risk behaviours for the age groups in what are known as survival charts. The impact of individual risk factors and their combined effect on mortality are visible at a glance. “In future, doctors will be able to refer to the easily comprehensible charts when giving health counselling to their patients in primary care”, comments Eva Martin-Diener with confidence. “Furthermore, they may also be important for the political discussions of prevention strategies for NCDs.”
The study was co-financed by the Swiss Heart Foundation and the Swiss Cancer League. It is an example of how cohort studies can generate relevant results for health policy.
Further reading:
Eva Martin-Diener, Julia Meyer, Julia Braun, Silvan Tarnutzer, David Faeh, Sabine Rohrmann and Brian W. Martin. The combined effect on survival of four main behavioural risk factors for non-communicable diseases. Preventive Medicine, June, 2014. DOI: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2014.05.023
Launch of the “National Strategy Prevention of Non-communicable Diseases”
The “National Dialogue Health Policy” – the permanent platform of the Swiss government and cantons – has decided to start drawing up a National Strategy for the Prevention of Non-communicable Diseases by 2016. The strategy aims to improve the population’s health competence and create health-promoting environments. The first part of the project covers the risk factors, national prevention activities and possible synergies for disease-specific strategies. The second part of the project concentrates on strengthening prevention in the health care system.
Contacts:
PD Dr. med. Brian Martin, MPH
Institute of Social and Preventive Medicine
University of Zurich
Tel. +41 79 285 15 92
Email: brian.martin@uzh.ch
PD Dr. med. David Fäh
Institute of Social and Preventive Medicine
University of Zurich
Email: david.faeh@ifspm.uzh.ch
044 634 46 16
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Largest magnetic anisotropy of a molecule measured at BESSY II
At the Berlin synchrotron radiation source BESSY II, the largest magnetic anisotropy of a single molecule ever measured experimentally has been determined. The larger this anisotropy is, the better a…

Breaking boundaries: Researchers isolate quantum coherence in classical light systems
LSU quantum researchers uncover hidden quantum behaviors within classical light, which could make quantum technologies robust. Understanding the boundary between classical and quantum physics has long been a central question…

MRI-first strategy for prostate cancer detection proves to be safe
Active monitoring is a sufficiently safe option when prostate MRI findings are negative. There are several strategies for the early detection of prostate cancer. The first step is often a…



