Analyzing Tumor Cells in Blood Using Nanomagnets
<br>
They have developed a prototype for the magnetic flow cytometry of blood. Blood is the most important source of diagnostic information for doctors tracking the success of therapy for a tumor or HIV. For their new process, the researchers are taking advantage of the GMR (giant magnetoresistance) effect, the discovery of which was the subject of the 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics.
In the field of medical diagnostics, an optical method of measurement for examining the characteristics of individual cells has existed for decades, remaining largely unchanged from the time it was developed. This method is known as flow cytometry, and can be used to identify specific cells, such as circulating tumor cells. Extracting cell data from whole blood, however, requires a time-consuming process. So the costs for traditional flow cytometry are too high for general clinical use or decentralized implementation, and growth in the market for this equipment has mostly been confined to the area of research.
But in the future, the new magnetic flow cytometry could offer a way of carrying out blood testing nearer to the patient (point-of-care), offering a method for specific cell detection in addition to a complete blood count. The scientists at Siemens Corporate Technology are employing GMR reading processes in combination with superparamagnetically marked cells.
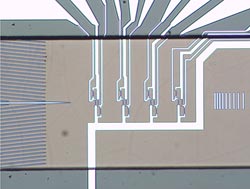
Their demonstration model, which is not yet ready for the market, can quantitatively detect specifically marked analytes in whole blood, without requiring pre-conditioning of the sample, such as the lysis (destruction) of red blood cells. Specifically, the marking of these analyte blood cells is accomplished using antibodies, which have superparamagnetic nanoparticles (beads) hanging on them. A magnet then attracts the marked cells, so that they are separated out and, like pearls on a string, they are counted by the GMR sensor.
This process enables the quantitative identification of tumor cells, for example. Through this special experimental design the researchers get four bits of information for each individual cell that is measured. With this information they can determine the cell's diameter and the speed at which it is moving – information which allows them to make accurate conclusions about whether it is a tumor cell or not.
Recently, the researchers showed that miniaturization of this kind of measuring system would be possible. For demonstrating this possibility in his bachelor's thesis, a researcher won the Innovation Prize for Applied Research from Regensburg University of Applied Sciences.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.siemens.com/innovationnewsAll latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Pinpointing hydrogen isotopes in titanium hydride nanofilms
Although it is the smallest and lightest atom, hydrogen can have a big impact by infiltrating other materials and affecting their properties, such as superconductivity and metal-insulator-transitions. Now, researchers from…

A new way of entangling light and sound
For a wide variety of emerging quantum technologies, such as secure quantum communications and quantum computing, quantum entanglement is a prerequisite. Scientists at the Max-Planck-Institute for the Science of Light…

Telescope for NASA’s Roman Mission complete, delivered to Goddard
NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is one giant step closer to unlocking the mysteries of the universe. The mission has now received its final major delivery: the Optical Telescope…



