Injecting gene cocktail into mouse pancreas leads to humanlike tumors
UT Health San Antonio scientist Dr. Bruno Doiron has invented a unique method to generate, in mice, pancreatic tumors that resemble human pancreatic cancer. This will be a tool researchers can use to develop new drugs that extend patients' lives, and it is a tool researchers have not had at their disposal before. Credit: Dr. Bruno Doiron/UT Health San Antonio
The technology could revolutionize studies of pancreatic cancer initiation and progression and spur new drug development. An article published in the journal Carcinogenesis (Oxford University Press) describes this unique approach. Results of the research were made available online in November 2017 ahead of peer-review and print publication in February 2018.
Scientists study pancreatic cancer by genetically engineering mice to develop the disease or by transplanting tumors into rodents to test drug activity. In both cases, the resulting tumors provide an artificial, rather than true, picture of the human disease, said the technology's inventor, Bruno Doiron, Ph.D., of UT Health San Antonio.
“For a decade, we have failed in treating pancreatic cancer because we didn't have a good way to test new drugs,” Dr. Doiron, an assistant professor in the Joe R. & Teresa Lozano Long School of Medicine, said.
Pancreatic cancer kills 95 percent of patients within five years of diagnosis. Advances in therapy have been negligible, with chemotherapies only able to extend survival by a few months. Need for a new study tool is therefore urgent.
Delivery method
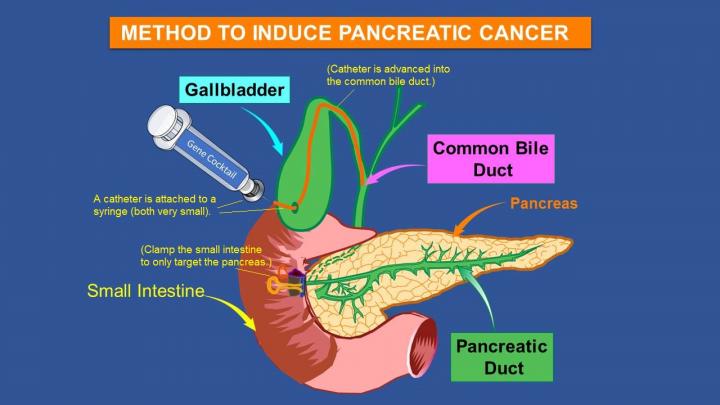
Dr. Doiron and his lab team are injecting a modified virus into the adult mouse pancreas. The virus is a delivery vehicle for two pro-cancer molecules (called KrasG12D mutation and shRNA p53) that are present in human pancreatic tumors.
Upon injection, the virus permeates the pancreas with these pro-cancer factors. The effect is contained; only the pancreas is altered by this molecular cocktail. When the mice reach 28 to 30 weeks of age, tumors develop that resemble human pancreatic cancer.
“I take the two major genetic mutations involved in human pancreatic cancer and inject them directly to the pancreas, and tumors develop in the adult mice,” Dr. Doiron said. “This bypasses the artificial manipulation introduced by other methods, and spontaneous cancers develop that mimic those found in people.”
The procedure is performed in mice that are not of any special breeding or stock. They are from many different parents. This ensures that the development of pancreatic cancer is in a random nature, the way it occurs in humans.
A step forward
The Carcinogenesis article “is an important paper for the field of pancreatic cancer, because it demonstrates that all previous methods of study are obsolete,” Dr. Doiron said.
Obesity and diabetes are major risk factors for pancreatic cancer. The risk of pancreatic cancer is increased 1.5-fold in obese subjects and two- to threefold in people with diabetes. The new technology can be used to delve into this link.
“The prevalence of obesity and Type 2 diabetes has reached epidemic proportions during the last two decades in the U.S. and worldwide, and this may explain, in part, why the death rate from pancreatic cancer has not declined in the same way as it has for some other cancers,” Dr. Doiron said.
Ruben A. Mesa, M.D., FACP, director of the Mays Cancer Center, the newly named center home to UT Health San Antonio MD Anderson Cancer Center, commented: “This important work by Dr. Doiron and colleagues will allow us to better predict which treatments for the devastating disease of pancreatic cancer will be effective. These discoveries are a much-needed advance on efforts to cure pancreatic cancer.”
###
About UT Health San Antonio
The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, with missions of teaching, research and healing, is one of the country's leading health sciences universities and is now called UT Health San Antonio™. UT Health San Antonio's schools of medicine, nursing, dentistry, health professions and graduate biomedical sciences have produced more than 33,000 alumni who are advancing their fields throughout the world. With seven campuses in San Antonio and Laredo, UT Health San Antonio has a FY 2018 revenue operating budget of $838.4 million and is the primary driver of its community's $37 billion biomedical and health care industry. For more information on the many ways “We make lives better®,” visit http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



