Is genetics the cause of mystery osteoporosis?
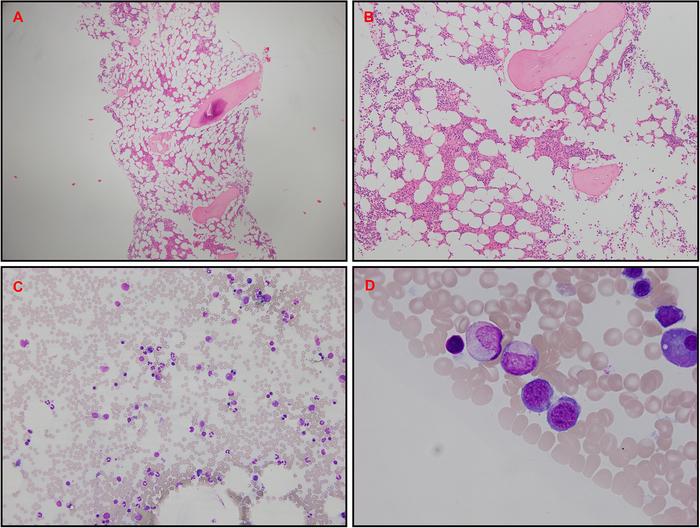
Bone marrow biopsy. (A and B) Hematoxylin and eosin trephine stain demonstrating mild to moderate hypocellular marrow (20%–30%) with moderately reduced erythropoiesis. (C and D) Aspirate demonstrating mild dyserythropoiesis with normal granulocytic and megakaryocytic lineages.
Credit: Hudson Institute of Medical Research
A recently discovered genetic mutation could be the cause of some severe and baffling cases of osteoporosis – including in young people.
The condition called idiopathic osteoporosis (IOP) occurs in younger adults and often involves bone fractures, even in patients with no history of physical trauma.
Head of Hudson Institute’s Metabolic Bone Research Group, Associate Professor Frances Milat, says the condition is often challenging to diagnose and treat due to factors including a poor understanding of the underlying cause, a lack of management guidelines, and limited research in this area.
“IOP has been associated with abnormal bone structure. It is thought that IOP patients may have a yet undiscovered genetic mutation that is responsible for their severe osteoporosis and multiple fractures,” said A/Prof Milat, who is also Deputy Director of Endocrinology at Monash Health.
Genetic variant behind unexplained osteoporosis
“Our team of clinicians and scientists identified a novel RUNX1 genetic variant in a young male patient that may have caused changes in bone structure and severe osteoporosis. This patient had suffered from multiple fractures with little or no trauma.
“This genetic mutation may be the cause of some cases of unexplained severe osteoporosis in young adults,” she said.
Finding genetic link opens care and therapy options
The research was published in the journal JBMR Plus. First author Dr Tomasz Block, an Advanced Trainee in Endocrinology at Monash Health, said the successful identification of underlying genetic causes of osteoporosis can lead to appropriate preventive care for patients, including surveillance and/or directed treatment to reduce the risk of a future fracture.
“This study gives insight into a potential genetic cause for unexplained severe osteoporosis and potential targeted therapy,” he said.
“In the case described, bone formation is potentially impaired by this mutation and therefore, the optimal treatment for this patient would be medications that stimulate new bone to form.”
What is idiopathic osteoporosis?
- Idiopathic osteoporosis (IOP) can adversely affect bone formation and bone resorption, often leading to abnormal bone structure and multiple atraumatic bone fractures.
- The mean age at diagnosis is 35 years and a family history of osteoporosis is common.
- The condition affects both males and females.
- Further research is needed to identify additional genetic and non-genetic causes of IOP.
Symptoms of idiopathic osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is called a ‘silent’ disease” because there are typically no symptoms until a bone is broken. Patients can present with:
- Back pain
- Loss of height
- Fractures or breaks, especially in the spine, hip, or wrist
- Stooped posture
- Difficulty standing or walking.
Treatments
While there is no known cure for idiopathic osteoporosis, there are several treatment options available to help manage the condition and prevent further bone loss.
Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage idiopathic osteoporosis. These include
- Regular exercise, particularly weight-bearing exercises
- A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D
- Quitting smoking
- Limiting alcohol consumption
Collaborators | Alfred Health, Monash Health
Journal information | Block TJ, Shore-Lorenti C, Zebaze R, Kerr PG, Kalff A, Perkins AC, Ebeling PR, Milat F. (2023) A Novel RUNX1 Genetic Variant Identified in a Young Male with Severe Osteoporosis. JBMR Plus. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm4.10791
Journal: JBMR Plus
DOI: 10.1002/jbm4.10791
Method of Research: Case study
Subject of Research: People
Article Title: A Novel RUNX1 Genetic Variant Identified in a Young Male with Severe Osteoporosis
Article Publication Date: 29-Jul-2023
Media Contact
Rob Clancy
Hudson Institute of Medical Research
communications@hudson.org.au
Cell: 0408579313
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



