Molecular sensor detects early signs of multiple sclerosis, Gladstone study finds
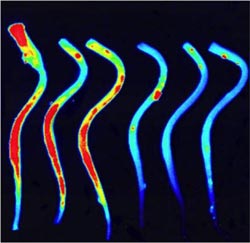
Using advanced detection and imaging techniques, Gladstone scientists were able to track thrombin activity in mice modified to mimic MS (left) compared to healthy controls.<br><br>Credit: Dimitrios Davalos/Kim Baeten/Katerina Akassoglou<br>
For some, the disease multiple sclerosis (MS) attacks its victims slowly and progressively over a period of many years. For others, it strikes without warning in fits and starts.
But all patients share one thing in common: the disease had long been present in their nervous systems, hiding under the radar from even the most sophisticated detection methods. But now, scientists at the Gladstone Institutes have devised a new molecular sensor that can detect MS at its earliest stages—even before the onset of physical signs.
In a new study from the laboratory of Gladstone Investigator Katerina Akassoglou, PhD, scientists reveal in animal models that the heightened activity of a protein called thrombin in the brain could serve as an early indicator of MS.
By developing a fluorescently labeled probe specifically designed to track thrombin, the team found that active thrombin could be detected at the earliest phases of MS—and that this active thrombin correlates with disease severity. These findings, reported online in Annals of Neurology, could spur the development of a much-needed early-detection method for this devastating disease.
MS, which afflicts millions of people worldwide, develops when the body's immune system attacks the protective myelin sheath that surrounds nerve cells. This attack damages the nerve cells, leading to a host of symptoms that include numbness, fatigue, difficulty walking, paralysis and loss of vision. While some drugs can delay these symptoms, they do not treat the disease's underlying causes—causes that researchers are only just beginning to understand.
Last year, Dr. Akassoglou and her team found that a key step in the progression of MS is the disruption of the blood brain barrier (BBB). This barrier physically separates the brain from the blood circulation and if it breaks down, a blood protein called fibrinogen seeps into the brain. When this happens, thrombin responds by converting fibrinogen into fibrin—a protein that should normally not be present in the brain. As fibrin builds up in the brain, it triggers an immune response that leads to the degradation of the nerve cells' myelin sheath, over time contributing to the progression of MS.
“We already knew that the buildup of fibrin appears early in the development of MS—both in animal models and in human patients, so we wondered whether thrombin activity could in turn serve as an early marker of disease.” said Dr. Akassoglou, who directs the Gladstone Center for In Vivo Imaging Research (CIVIR). She is also a professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, with which Gladstone is affiliated. “In fact, we were able to detect thrombin activity even in our animal models—before they exhibited any of the disease's neurological signs.”
In laboratory experiments on mice modified to mimic the signs of MS, the team employed an Activatable Cell-Penetrating Peptide (ACPP), a special type of molecular probe that delivers fluorescent agents to a region of interest. For this study, they developed a thrombin-specific ACPP that could track thrombin activity in mice as the disease progressed. They then carefully analyzed where—and at what stage of disease—thrombin activity was found.
“We detected heightened thrombin activity at specific disease 'hot-spots,' regions where neuronal damage developed over time,” said Gladstone Staff Research Scientist Dimitrios Davalos, PhD, associate director of the CIVIR and one of the paper's lead authors. “And when we compared those results to those of a separate, healthy control group of mice, we saw that thrombin activity in the control group was wholly absent.”
“Our results are proof of principle that a thrombin-specific molecular probe could be used as an early-detection method,” added former Gladstone Postdoctoral Researcher Kim Baeten, PhD, the paper's other lead author.
The team's results offered significant support for the notion that thrombin activity is directly tied to the degradation of nerve cell's myelin sheath—and the subsequent destruction of nerve cells—that characterizes MS. But they also shed light on what has been a long-standing mystery: the underlying molecular processes that kick-start the progression of MS.
“In the future,” said Dr. Akassoglou, “this thrombin-specific ACPP could be developed to one day allow for early patient diagnosis and therapeutic intervention—including a way to effectively monitor how patients are responding to the latest treatments.”
Jae Kyu Ryu, PhD, Dimitri Smirnoff, Mark Peterson, MD, and Catherine Bedard also participated in this research at Gladstone, which received support from the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, the Nancy Davis Foundation for Multiple Sclerosis Research, the Pediatric Scientist Development Program, the March of Dimes and the National Institutes of Health (Grants NS052189 and NS066361).
About the Gladstone Institutes
Gladstone is an independent and nonprofit biomedical-research organization dedicated to accelerating the pace of scientific discovery and innovation to prevent, treat and cure cardiovascular, viral and neurological diseases. Gladstone is affiliated with the University of California, San Francisco.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.gladstone.ucsf.eduAll latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…

ASXL1 Mutation: The Hidden Trigger Behind Blood Cancers and Inflammation
Scientists show how a mutated gene harms red and white blood cells. LA JOLLA, CA—Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have discovered how a mutated gene kicks off…



