This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.

Long-term exposure to the weightless environment of space has significant effects on astronaut physiology, notably changing the skeleton and muscle. To meet the requirements of long-stay missions aboard the International Space Station, the European (ESA), French (CNES) and Japanese (NASDA) space agencies are jointly conducting ground-based research to evaluate ways of countering the adverse effects.
Countermeasures are tested on the healthy subject using an experimental model reproducing t

Results of a UK study in this week’s issue of THE LANCET suggest that the antianginal drug nicorandil could reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease associated with angina.
Angina occurs in 10% of men aged older than 60 years in the UK (10-15 years later in women), and is a common underlying cause of coronary heart disease (CHD). Aspirin, angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and statins reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in subgroups of patients with stable angina; however,
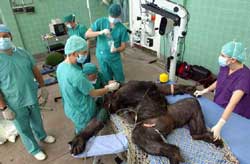
Romina, a female Western lowland gorilla at Bristol Zoo Gardens, has successfully undergone pioneering surgery to restore her sight in the first ever cataract operation performed in Europe on an adult gorilla. Born with cataracts, 21-year-old Romina underwent the two-hour procedure at the University of Bristol`s Veterinary Hospital in March and, for the first time in her life, she can now see the world around her clearly.
Romina was born at Rome Zoo and hand-reared. Before her arrival in the UK

Life-threatening pneumonia in bone marrow transplant (BMT) patients can be controlled using a strategy called pre-emptive therapy, scientists heard today (Wednesday 10 April 2002) at the spring meeting of the Society for General Microbiology at the University of Warwick.
“We have found that early diagnosis and treatment of colds and flu in transplant and immunocompromised patients can reduce the risk of pneumonia. But pre-emptive therapy is not just a question of providing drugs to patients.

Epilepsy drugs given to women during pregnancy can treble the risk of congenital malformation or developmental delay in their children, finds research in the Journal of Medical Genetics.
Stopping treatment for epilepsy during pregnancy is not an option, but there is an urgent need to develop safer drugs, conclude the researchers. Six in every 1000 pregnancies will be to a woman treated with epilepsy drugs.
One hundred and forty nine mothers being treated with antiepileptic drugs in

There is a strong genetic component to the gluten intolerance disorder, coeliac disease, shows research in Gut.
In the largest study of its kind, Italian researchers studied 47 twin pairs, who were selected on the basis that one belonged to the Italian Coeliac Disease Association (AIC). They were tested for antibodies specific to coeliac disease to ensure that ‘silent’ disease was detected, and their genetic profile was mapped. Tissue samples were taken to confirm changes indicative of the