Parkinson’s gene may impair how new neurons are made throughout our lifetime
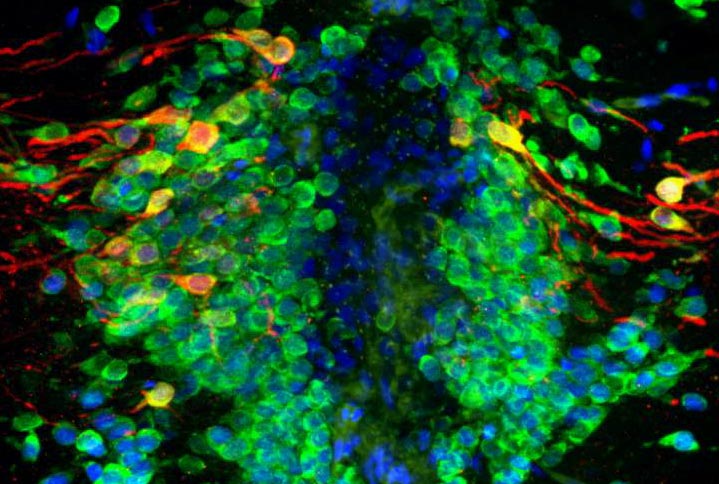
Old (green) and newly made (orange) dopamine-producing nerve cells in the zebrafish brain
Credit: University of Sheffield
A pioneering study, published in Scientific Reports, found that the Parkinon’s gene PINK1 is important for the generation of dopamine-producing neurons throughout life, and is not just responsible for the premature death of these neurons.
The international research, led by University of Sheffield’s Neuroscience Institute, used two model systems to examine how neurons are produced throughout our lifetime Parkinson’s disease is a relentlessly progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects around 145,000 people in the UK A gene defect linked to Parkinson’s disease may not only cause the early death of neurons, but also impair the process that generates neurons in the brain throughout our lifetime, a new study has revealed.
The international study, led by the University of Sheffield’s Neuroscience Institute, may have a significant impact on the future treatment of Parkinson’s patients who develop the illness due to PINK1 defect or similar gene defects.
The development of novel treatments and therapies to slow down disease progression, halt or reverse Parkinson’s may now focus on enhancing the generation of new dopamine-producing neurons, rather than just trying to protect these neurons from dying later.
The findings, published today (23 March 2021) in Scientific Reports, used two model systems to measure how inactivation of the PINK1 gene affects dopamine-producing neurons in the adult brain.
Dopamine-producing neurons are the most severely affected brain cells in Parkinson’s disease. It is typically thought that Parkinson’s genes, such as PINK1, cause early death of these neurons, with symptoms developing when neuron numbers fall. However, here, researchers found that a deficiency in PINK1 resulted in fewer dopamine-producing neurons being made throughout life.
Professor Oliver Bandmann, Professor of Movement Disorders Neurology at the Sheffield Institute for Translational Neuroscience (SITraN), said: “Neurogenesis is the process by which new neurons are formed in the brain. Recent evidence suggests that this process is ongoing throughout life but the relevance of this is poorly understood in neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease.”
“We know that mutations in the PINK1 gene cause an early onset, inherited form of Parkinson’s disease. If we can further our understanding about the impact of this genetic mutation on the dopamine-producing neurons we can develop new therapeutic approaches that aim to mitigate those effects.”
In collaboration with the University of Luxembourg, researchers used two complementary model systems to examine how neurons are reproduced throughout our lifetime.
Professor Marysia Placzek, Professor of Developmental Neurobiology in the Department of Biomedical Science, said: “This study attests to the power of using simple model organisms for pre-clinical translational research. We used the zebrafish to demonstrate that dopamine-producing neurons are generated into adulthood at a rate that decreases with age and that PINK1-deficiency impairs neurogenesis of these neurons, significantly in early adult life. Our international collaborators then confirmed these results in a human organoid cell model.”
The observation of impaired adult dopaminergic neurogenesis in PINK1 deficiency in two complementing model systems may have significant consequences for future therapeutic approaches in Parkinson’s disease. Future research will aim to identify the precise mechanisms that link Parkinson’s genes to neurogenesis. This will allow us to explore the development of gene therapy or small molecule approaches to enhance neurogenesis in the brain of patients with Parkinson’s. The development of new therapies for brain diseases like Parkinson’s is the main focus of the Sheffield Institute for Translational Neuroscience (SITraN).
The research was funded by the Medical Research Council (MRC), Parkinson’s UK and the Wellcome Trust.
Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease, with approximately 10 million people affected worldwide. Currently, only symptomatic treatment options are available to patients.
The University of Sheffield launched a sustained fundraising effort for Parkinson’s disease research at the end of 2019. Since then, Sheffield staff, students, alumni and the general public have come together to raise more than £350,000 so far. The ongoing efforts of this campaign are set to continue as Sheffield dedicates itself to backing the next breakthrough.
###
To find out more and make a gift, please visit:
https:/
The research forms part of the work of the University of Sheffield’s Neuroscience Institute, which aims to bring academics and scientists together from across varied specialties to translate scientific discoveries from the lab into pioneering treatments that will benefit patients living with neurodegenerative disorders.
Media contact: Amy Huxtable, Media Relations Officer, University of Sheffield, a.l.huxtable@sheffield.ac.uk
Notes to editors:
The University of Sheffield
With almost 29,000 of the brightest students from over 140 countries, learning alongside over 1,200 of the best academics from across the globe, the University of Sheffield is one of the world’s leading universities.
A member of the UK’s prestigious Russell Group of leading research-led institutions, Sheffield offers world-class teaching and research excellence across a wide range of disciplines.
Unified by the power of discovery and understanding, staff and students at the university are committed to finding new ways to transform the world we live in.
Sheffield is the only university to feature in The Sunday Times 100 Best Not-For-Profit Organisations to Work For 2018 and for the last eight years has been ranked in the top five UK universities for Student Satisfaction by Times Higher Education.
Sheffield has six Nobel Prize winners among former staff and students and its alumni go on to hold positions of great responsibility and influence all over the world, making significant contributions in their chosen fields.
Global research partners and clients include Boeing, Rolls-Royce, Unilever, AstraZeneca, Glaxo SmithKline, Siemens and Airbus, as well as many UK and overseas government agencies and charitable foundations.
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Parallel Paths: Understanding Malaria Resistance in Chimpanzees and Humans
The closest relatives of humans adapt genetically to habitats and infections Survival of the Fittest: Genetic Adaptations Uncovered in Chimpanzees Görlitz, 10.01.2025. Chimpanzees have genetic adaptations that help them survive…

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…



