Study aims to revolutionise chest physiotherapy to babies and children
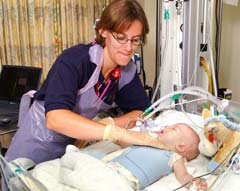
Senior Physiotherapist Tracey Pond uses the new sensing mat in the Paediatric Intensive Care Unit at Southampotn General Hospital
A new device being developed by researchers at the University of Southampton and Great Ormond Street Hospital is designed to optimise the effectiveness of chest physiotherapy techniques on babies and children suffering from breathing difficulties.
Rachael Gregson, a Research Fellow at the University’s School of Medicine and Great Ormond Street Hospital is leading the research and has developed an innovative sensing mat to measure chest physiotherapy.
Rachael says that although chest physiotherapy has been in use for over 40 years, treatments may vary significantly among practitioners leading to differing levels of effectiveness: ‘Current techniques used are unquantified and their effects on the child’s breathing have not been fully assessed. The sensing mat we have designed is fixed over the child’s chest wall and will measure the pressure between the hand giving the physiotherapy and the chest wall. The child’s breathing will be monitored before, during and after the treatment to discover any changes.’
‘Once we find out which techniques are most effective, the information could then be used in future clinical trials of best practice. We hope the early prototype machine can be refined and streamlined for use as a teaching aid both in hospitals and the home environment. By optimising the physiotherapy techniques in use, children will hopefully enjoy a swifter recovery,’ adds Rachael Gregson.
Children in the intensive care units at both Southampton General Hospital and Great Ormond Street Hospitals will be involved in this multicentre collaboration. A grant from the medical research charity ‘Sport Aiding medical Research for KidS’ (SPARKS) will enable the sensing system to be modified for use in older children.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



