Simplified method to modify disease signaling with light
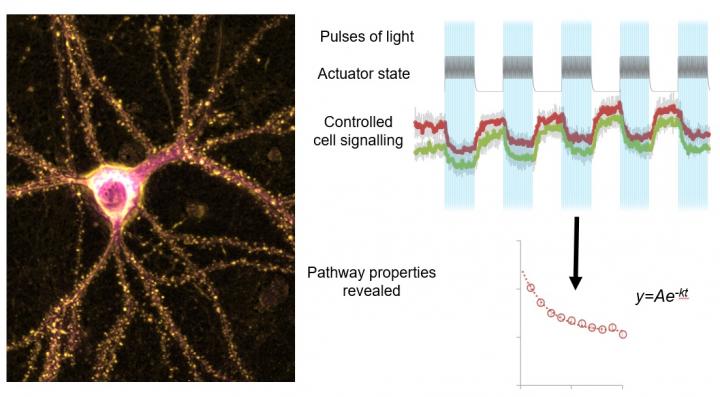
Expression of optogenetic actuators in neurons allows precise non-invasive control of signalling pathways using light pulses. This permits a better understanding of pathway modified in neurological disorders. Adapted from https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18816-8 under CC-BY-4.0
Credit: Michael Courtney
Most diseases are caused by aberrant cell signaling processes and basic research in cell signaling is needed to identify targets for future therapeutic approaches, especially in cases where no cures or effective treatments are currently available.
Cellular optogenetics uses light to precisely control cell signaling in space and over time, making it an invaluable technique for disease research. However, this potentially revolutionary method has been difficult for many researchers to use as, over long periods of time, the used light can itself have adverse effects on biological systems and the optogenetic tools can inactivate unexpectedly rapidly.
Now, researchers from the University of Turku in Finland, in collaboration with Frankfurt University Hospital in Germany, have developed a novel way to harness the quantum mechanical phenomenon of resonance energy transfer to design optogenetic tools that are more sensitive to light. The new method also informs the user exactly when an optogenetic tool is going to inactivate in cells. If continued activity is required, just the right amount of additional light can then be re-applied to re-activate the tool.
Combining these advances with existing tools and knowledge, the researchers were able to design and build more efficient optogenetic tools to investigate signaling pathways. With the improved tools, they studied two common chemotherapy drugs known to cause side effects on neurons and cause neuropathic pain. The new tools revealed how both activatory and inhibitory pathways contribute to the actions of these drugs on the investigated disease-associated pathway.
“Now we can develop more powerful tools to understand precisely how harmful conditions disrupt signaling in living cells. This information is likely to help us in identifying targets and designing better therapeutic compounds for conditions such as chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain,” says Lili Li, the lead author of the study and Postdoctoral Researcher at the Turku Bioscience Centre.
“There is still considerable potential to further exploit these quantum mechanical phenomena to devise even better quantitative and informative methods in biology and medicine, which could support the future discovery of new therapeutic approaches,” adds senior author of the study Michael Courtney.
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

An Endless Loop: How Some Bacteria Evolve Along With the Seasons
The longest natural metagenome time series ever collected, with microbes, reveals a startling evolutionary pattern on repeat. A Microbial “Groundhog Year” in Lake Mendota Like Bill Murray in the movie…

Witness Groundbreaking Research on Achilles Tendon Recovery
Achilles tendon injuries are common but challenging to monitor during recovery due to the limitations of current imaging techniques. Researchers, led by Associate Professor Zeng Nan from the International Graduate…

Why Prevention Is Better Than Cure—A Novel Approach to Infectious Disease Outbreaks
Researchers have come up with a new way to identify more infectious variants of viruses or bacteria that start spreading in humans – including those causing flu, COVID, whooping cough…



