Researchers identify “hot spots” for developing lymphatic vessels
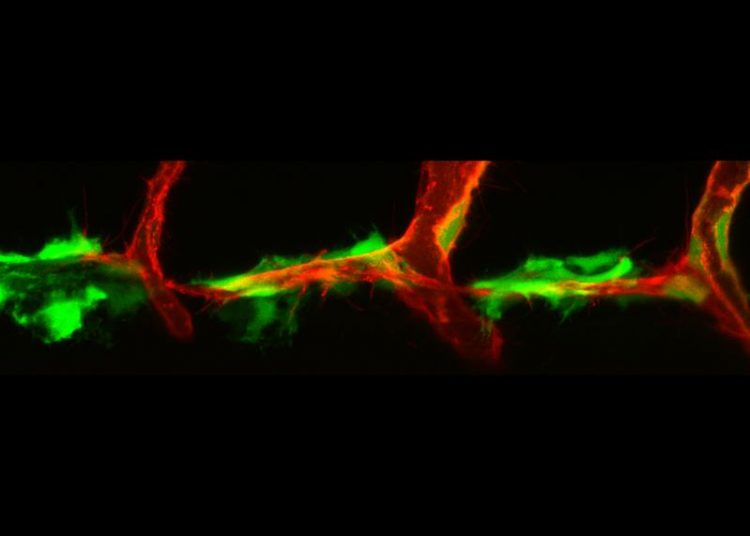
Developing lymph vessels in zebrafish: cells of the connective tissue (fibroblasts, green) express the protein VEGF-C and influence the migration of lymphatic endothelial cells (red). Andreas van Impel
When an embryo develops, a wide variety of proteins and enzymes trigger a series of biochemical reactions. The development of the lymphatic vasculature is crucially dependent on one specific protein – the growth factor VEGF-C.
In order to become biologically active and to initiate downstream signalling events, the protein must first undergo processing steps. Thus far it was unclear, however, how and where the necessary factors come together that are required for VEGF-C activation, and which cell types provide these individual factors during development.
Using the zebrafish model, an international team of researchers has now gained new insights into how and at which spots the individual protagonists of the VEGF-C signalling pathway need to interact with each other in the embryo, in order to allow proper lymphatic vasculature development.
The researchers identified special cells in the connective tissue that, at defined spots in the embryo, produce the important protein VEGF-C itself, as well as two -protein-processing enzymes which can activate the VEGF-C protein. In the case of one of these proteins, it was previously completely unknown that it had this function.
“The cells we have identified, the fibroblasts, represent what appear to be ‘hot spots’ for the occurrence of the activated protein,” says Dr. Andreas van Impel from the University of Münster, who led the study. The results provide not only fundamental new insights into how the lymphatic system develops, but also, conversely, has relevance for human diseases.
If the signalling pathway is miss-regulated in humans, genetically caused forms of lymphoedema will develop. Also, cancer cells can employ the lymphatic vessels to metastasize.” If it turns out that a comparable fibroblast population is present in humans as well, our findings could impact future approaches to treat a variety of lymphatic related diseases,” says Andreas van Impel. The study has been published in the journal “Nature Communications”.
Background and method:
Worldwide, there are around a thousand groups of researchers working with zebrafish. These fish are suitable to investigate how an organism develops – including the bones, blood vessels and the lymphatic system. As fish embryos develop outside the womb and are transparent for a few days, the researchers can precisely monitor changes in development and identify connections with humans.
In their current study, the researchers investigated the protein VEGF-C, which is important for lymphatic vessel growth. In order for it to become biologically active, it has to be processed which means parts of the protein need to be cleaved off.
VEGF-C can only bind and activate its receptor once two so-called pro-domains have been removed. The enzymes which process the protein are called proteases. In their study, the researchers examined the role of the secreted proteases ADAMTS3 and ADAMTS14 during the activation of VEGF-C.
Using state-of-the-art confocal microscopy, the researchers showed that embryos lacking both proteases as a result of genetic mutations fail to form lymphatic vessels – which led the researchers to conclude that the processing of VEGF-C can be carried out not only (as previously assumed) by ADAMTS3, but also by the related protease ADAMTS14.
This was something that the researchers found not only for the zebrafish proteins, but also in experiments with human cell culture lines. “Our observations indicate that this ability of the ADAMTS14 protein is conserved through evolution,” says lead author Guangxia Wang, who is writing her PhD thesis at the CiM-IMPRS Graduate School at Münster University. The School is part of the “Cell Dynamics and Imaging” research focus.
In cell transplant experiments, the researchers were able to show that certain neuronal structures, as well as fibroblasts, represent the cellular sources for both proteases and, in addition, for the VEGF-C protein. “Activating the VEGF-C protein in these positions in the embryo was sufficient to trigger normal development of lymphatic vessels, which again emphazises the importance of this cell population for the regulation of lymphangiogenesis,” says Andreas van Impel.
The researchers plan to undertake further investigations to find out how relevant the activity of ADAMTS14 is for the development and maintenance of the lymphatic system in mammals. “As mutations in the ADAMTS3 protease lead to diseases in humans, it seems reasonable to assume that ADAMTS14 is also a candidate gene for human syndromes,” says group leader Prof. Stefan Schulte-Merker.
Furthermore, the researchers would like to assess whether a comparable fibroblast population is also present in mice and humans which also synthesizes all – or at least some – of the proteins that play a central role in processing and consequently in controlling the activity of the VEGF-C signalling pathway.
Funding and institutions involved:
The institutions involved in the study were, in addition to the University of Münster, the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Biomedicine in Münster, the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, the University of Heidelberg, the German Centre for Cardiovascular Research in Heidelberg and Mannheim, the Hubrecht Institute in Utrecht (Netherlands), the Karolinska Institute in Huddinge and the University of Uppsala (both Sweden) and the University of Liège (Belgium). The study received financial support from the German Research Foundation as part of the Research Group 2325 “Interactions at the Neurovascular Interface” and of the Collaborative Research Centre 1348 “Dynamic Cellular Interfaces”.
Dr. Andreas van Impel (University of Münster)
Email: vanimpel@uni-muenster.de
Phone.: +492519802874
G. Wang et al. (2020): Specific fibroblast subpopulations and neuronal structures provide local sources of Vegfc-processing components during zebrafish lymphangiogenesis. Nature Communications; DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16552-7
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-16552-7 Original publication in “Nature Communications”
https://www.medizin.uni-muenster.de/icor/ Research group Prof. Stefan Schulte-Merker at Münster University
Research focus “Cell dynamics and imaging” at Münster University https://www.uni-muenster.de/forschung/en/profil/schwerpunkt/zelldynamik.html
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Pinpointing hydrogen isotopes in titanium hydride nanofilms
Although it is the smallest and lightest atom, hydrogen can have a big impact by infiltrating other materials and affecting their properties, such as superconductivity and metal-insulator-transitions. Now, researchers from…

A new way of entangling light and sound
For a wide variety of emerging quantum technologies, such as secure quantum communications and quantum computing, quantum entanglement is a prerequisite. Scientists at the Max-Planck-Institute for the Science of Light…

Telescope for NASA’s Roman Mission complete, delivered to Goddard
NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is one giant step closer to unlocking the mysteries of the universe. The mission has now received its final major delivery: the Optical Telescope…



