Physicists find ways to control gamma radiation
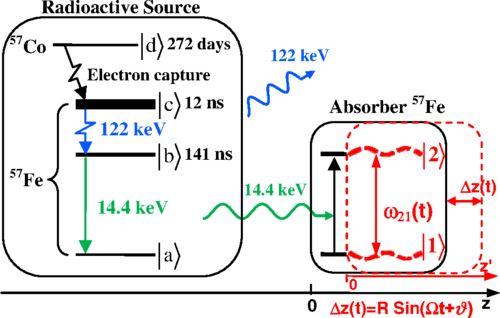
Energy scheme of the radioactive source of 14.4 keV photons and the vibrating absorber used in the experiment. The 57Co nuclei (left side) in the state |d⟩ decay to 57Fe nuclei in the excited state |c⟩ (with a half-life of T1/2≈272 day), followed by cascade decay: |c⟩→|b⟩ (with decay time T≈12 ns) and |b⟩→|a⟩ (with decay time TS≈141 ns) with emission of 122 and 14.4 keV photons (shown by blue and green lines), respectively. Depolarized recoilless 14.4 keV photons ( λ≈0.86 Å) resonantly interact with transition |1⟩→|2⟩ of 57Fe nuclei when propagating through the single-line 57Fe absorber (right side). They are resonantly absorbed in motionless absorber (black lines). Harmonic vibration of the absorber as a whole (pistonlike vibration) with circular frequency Ω, amplitude R, and initial phase ϑ along the photon propagation direction (marked in red) leads to periodic temporary variation in |1⟩→|2⟩ transition frequency ω21(t) (dashed red curves) due to the Doppler effect. It modifies the interaction of the photon with absorber and can result in AIT (see Fig. 2 and text). The axis z labels the laboratory reference frame, red axis z' labels the reference frame of the vibrating absorber, and Δz=z−z'. Credit: Kazan Federal University
Researchers from Kazan Federal University, Texas A&M University and Institute of Applied Physics (Russian Academy of Sciences) found ways to direct high frequency gamma radiation by means of acoustics.
The paper describes an optical “switch” – a device able to let through or stop gamma quanta by switching the acoustic field. Basically, the mechanism makes iron “transparent” for gamma rays when needed.
Mossbauer Spectroscopy Lab of Kazan Federal University showed acoustically induced transparency of a resonant medium for gamma radiation in an experiment.
The essence of this phenomenon lies in the transformation of the spectrum of the absorption line into a comb structure consisting of satellite lines spaced from the main line by the frequency of the acoustic field.
For the experiment, gamma quanta with an energy of 14.4 keV were used, which are emitted during the decay of the excited state of the iron-57 nucleus.
“By acting on the absorber containing the Fe-57 nuclei with the help of a piezoelectric transducer, it was possible to achieve for the optically dense absorber to become transparent to resonant gamma rays. The absorber was attached to a piezoelectric transducer, which vibrated at a certain frequency and amplitude.
At an oscillation amplitude corresponding to a modulation index of 2.4, the absorption of photons with an energy of 14.4 keV was suppressed 148 times,” explains Mossbauer Spectroscopy Lab Head Farit Vagizov.
“This effect is analogous to the effect of electromagnetically induced transparency in optics, when radiation in one frequency range is used to control electronic transitions of atoms in another frequency range.
As you know, the effect of electromagnetically induced transparency in atomic media has a fairly wide area of potential applications: the creation of controlled delay lines, devices for recording and reproducing quantum information, frequency standards in atomic clocks, and much more.”
This effect showed that with the help of low-frequency (~10-40 MHz) acoustic excitation, it is possible to control the process of transmission of high-frequency electromagnetic radiation with a frequency of more than 1013 MHz through the resonant medium. This effect may turn out to be useful for controlling the generated radiation on modern synchrotron sources and X-ray lasers, as well as for creating promising quantum devices.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Pinpointing hydrogen isotopes in titanium hydride nanofilms
Although it is the smallest and lightest atom, hydrogen can have a big impact by infiltrating other materials and affecting their properties, such as superconductivity and metal-insulator-transitions. Now, researchers from…

A new way of entangling light and sound
For a wide variety of emerging quantum technologies, such as secure quantum communications and quantum computing, quantum entanglement is a prerequisite. Scientists at the Max-Planck-Institute for the Science of Light…

Telescope for NASA’s Roman Mission complete, delivered to Goddard
NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is one giant step closer to unlocking the mysteries of the universe. The mission has now received its final major delivery: the Optical Telescope…



